Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Lybra DAO
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Lybra DAO
The Lybra DAO is the governing DAO of Lybra Finance, a decentralized finance platform that provides stablecoin management. Holders of esLBR tokens can submit proposals and participate in voting, where the extent of their voting influence is proportionate to the number of governance tokens they possess. [2]
Overview
Launched in October 2023, the Lybra DAO is the central element in Lybra Finance's decision-making framework. Governance responsibilities within the Lybra DAO are delegated to LBR token holders, providing them the power to influence the project's direction, propose and engage in decision-making procedures, and collectively supervise the protocol. This community-driven approach aims to maintain the decentralized nature of the Lybra Finance project, ensuring that its development aligns with the well-being and preferences of its user base. [1]
Governance
Voting Power
Participants of the Lybra DAO can accumulate voting power through two methods: [1]
- Accumulating esLBR: The esLBR token functions as a governance tool within the Lybra DAO, and users have the option to acquire it through different methods, including minting eUSD or peUSD, providing liquidity to various pools, and staking LBR.
- Buying Discounted esLBR: Lybra's Bounty Mechanism enables users to purchase discounted esLBR tokens using LBR tokens or eUSD.
Submitting Proposals and Voting
Users are required to have a minimum of 100,000 esLBR to submit a proposal. Users initially post about the proposal in the Lybra Discord and then move to Tally, a front-end for on-chain DAOs. [1]
Once the proposal is submitted, voting takes place two days later and lasts seven days. One LBR is equal to one vote, and any holder of esLBR is allowed to participate. [1]
Voting Process
Lybra DAO has two voting processes for off-chain proposals and on-chain proposals. Voting for off-chain proposals takes place on Snapshot, while on-chain proposal voting takes place on Tally. [3]
Off-chain Proposals
Off-chain proposals refer to situations where no existing contract or codebase is prepared for deployment through Time Lock. Users can vote on these proposals through Snapshot, a platform allowing DAOs, DeFi protocols, or NFT communities to vote without paying gas fees. [3]
To submit an off-chain proposal, users need to have $10k worth of esLBR, and to participate in voting on an Off-Chain proposal, a minimum of one esLBR is required, where each esLBR equates to one vote. LBR must be staked as esLBR before the vote to be eligible, and any alterations after proposal creation, such as cancellation or unstaking, will only impact future proposals. [3]
On-chain Proposals
On-chain proposals involve having a pre-existing contract or codebase for deployment through Time Lock. Users can vote on Tally, a front-end for on-chain DAOs. [3]
Users need 100k esLBR to raise an on-chain proposal. Voting is also the same as off-chain proposal voting. One esLBR equals one vote, and LBR must be staked as esLBR before being eligible to vote. However, the difference with on-chain proposal voting is that Tally requires approval of a minimum of 4% of the total circulating supply of esLBR. [3]
Lybra Wars
The transition to a DAO governance structure empowered Lybra governance token holders to influence pivotal decisions, including matters related to Liquid Staking Token (LST) pools within the Lybra protocol. The Lybra Wars emerged, allowing LST pools to incentivize esLBR holders through token rewards based on their voting power, fostering a competitive ecosystem. [4]
The protocol introduced a new bribing mechanism, enabling LST pools to motivate esLBR holders with token rewards corresponding to their voting power. Increased esLBR votes for a pool elevated its significance, escalating esLBR emissions and attracting more deposits. The Lybra Wars, fostering competition among LST pools for esLBR emissions, aim to create a mutually beneficial scenario, contributing to decentralization and providing engaging incentives for stakeholders participating in governance decisions. [4]
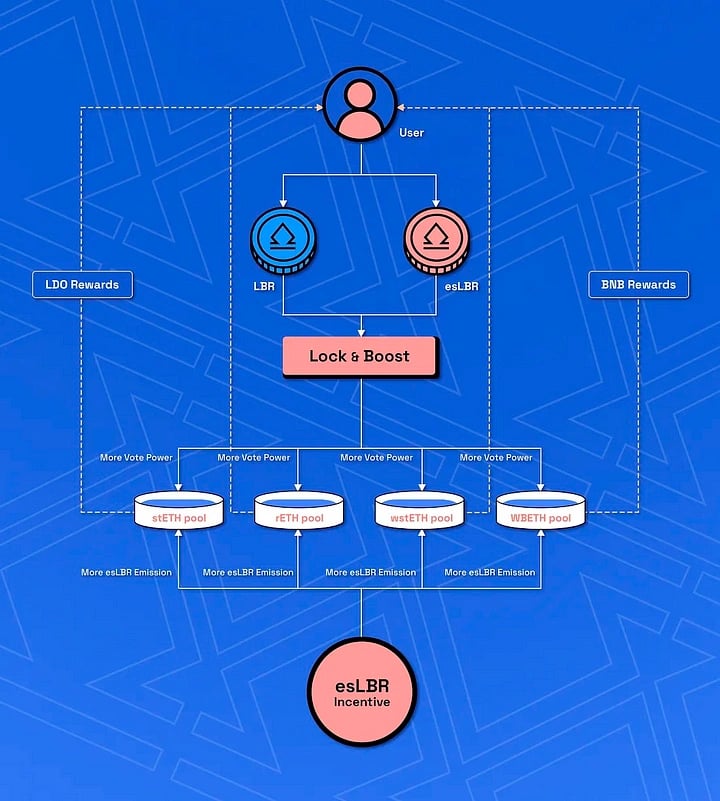
Driving Value
The Lybra Wars increases the value of esLBR and LBR tokens in five ways: [4]
- Additional Yields via Bribes
- The rewards for holders are tied to the level of voting power they commit to directing esLBR emissions to a specific LST pool. Holding more esLBR corresponds to increased voting power and greater potential earnings from incentives. Consequently, the bribes distributed through the Lybra Wars introduce a new income source, enhancing overall yields.
- Increased Demand for Tokens
- The Lybra DAO permits LST projects not currently integrated into Lybra to propose the inclusion of their asset by submitting a proposal to the DAO. For off-chain proposals, a minimum of $10,000 worth of esLBR is required, while on-chain proposals necessitate 100,000 esLBR. This incentivizes LST projects to acquire substantial amounts of Lybra governance tokens for proposal submission. Consequently, this introduces a significant demand for LBR / esLBR within the Lybra ecosystem, contributing to the tokens' value support.
- Reduced Availability of LBR
- To obtain voting power and be eligible for bribes in the Lybra Wars, LBR holders must stake their tokens, transforming them into esLBR. This action diminishes the quantity of unstaked LBR in circulation, contributing additional support to its value.
- New Partner Protocols
- The novel governance and bribing dynamics open avenues for developing various entities, including Lybra governance aggregation protocols and incentive-boosting layers. Each of these entities has the potential to attract new audiences and introduce additional sources of demand into the Lybra ecosystem.
- Decentralized Structure for LST Projects
- The Lybra Wars dynamic enables the protocol to maintain LST agnosticism while incentivizing LST projects to devise effective strategies for attracting volume. Each LST project is driven to minimize its churn while simultaneously increasing the churn of other LST tokens within the protocol. Collaboration among different projects may also occur to achieve broader influence. This introduces diverse strategies for LST projects, all inherently designed to benefit governance token holders, while the protocol maintains a neutral position.
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
