Osaka Protocol
Osaka Protocol, launched on April 23, 2023, seeks to restore the principles of true decentralization. With no developer supply or preferential access for early participants, _t_he protocol emphasizes fairness by counterbalancing early claims with broader distribution. This approach aims to create a collaborative ecosystem rooted in shared ownership and collective progress, embodying the ideals of transparency and trustlessness originally envisioned in the DeFi space. [4]
Overview
Osaka Protocol is a decentralized finance project designed to foster shared responsibility and equality, where ownership percentage reflects an individual’s influence and accountability. Inspired by Shiba Inu’s vision of decentralization, it operates on Ethereum with a fixed ERC-20 contract and employs a deflationary model by burning 50% of its initial supply. Tokens are distributed via airdrops and liquidity incentives to encourage community involvement. While it faces challenges like sustaining engagement without centralized control, Osaka Protocol emphasizes transparency and collaboration, aiming to establish a thriving, community-driven ecosystem. [1] [2] [3]
Features
Inspired by Shiba Inu, Osaka Protocol adopts a deflationary model by burning 100% of its intellectual property and 50% of its token supply at launch. This mechanism reduces supply over time, fostering scarcity and potentially increasing token value.
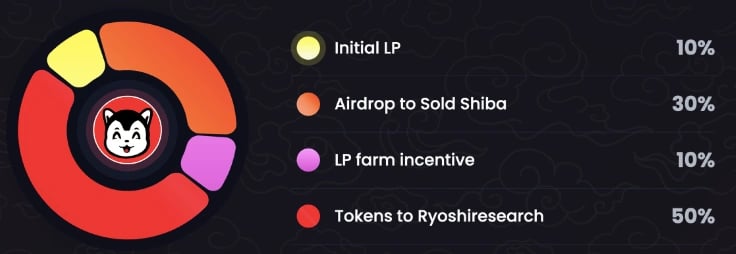
Liquidity provision is incentivized through rewards for users participating on platforms like Uniswap. This approach supports liquidity, enhances trading activity, and strengthens the protocol's ecosystem.
Tokens are distributed via airdrops to early supporters and active participants. This ensures equitable distribution, encourages engagement, and promotes broader adoption.
The protocol maintains transparency in token distribution, with clear allocations for liquidity, airdrops, and farming incentives. This openness fosters trust and ensures equitable management of resources.
Consensus Mechanism
Osaka Protocol employs a governance model where token holders can propose and vote on decisions. Voting power is proportional to each holder's stake, ensuring governance reflects collective input while maintaining a decentralized structure.
To encourage engagement, active participants in governance activities, such as voting or submitting proposals, are rewarded with tokens or other incentives. This approach promotes an active and committed community.
The protocol incorporates stakeholder feedback collected through surveys, discussions, and voting. This approach ensures governance remains responsive to community needs and priorities.
Users can stake tokens to participate in governance, with voting power proportional to the staked amount. This model encourages long-term commitment and active participation in decision-making. [1]
Tokenomics

Osaka Protocol Token (%OSAK)
Osaka Protocol's $OSAK token mirrors the supply model of the original Shiba Inu and is based on a fixed, immutable ERC-20 contract that cannot be altered or exploited. The token is Omnichain-enabled, utilizing LayerZero's OFT (Omnichain Fungible Token) standards. A dedicated OFT Bridge Adapter on Ethereum facilitates cross-chain transfers by securely holding $OSAK tokens for bridging across multiple blockchain networks. [5]
Token Supply