Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Symbiotic
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Symbiotic
Symbiotic is a shared security protocol that aims to help network builders manage restaking and enhance security while allowing users to compound interest rewards.[1][2]
Overview
Launched on June 11, 2024, by Misha Putiatin and Algys Ievlev, Symbiotic is a shared security protocol designed to serve as a coordination layer for (re)staking management in a permissionless environment. The protocol aims to allow networks to oversee aspects such as collateral, node operations, rewards, and slashing mechanisms, while providing the option for participants to opt in or out of shared security arrangements.
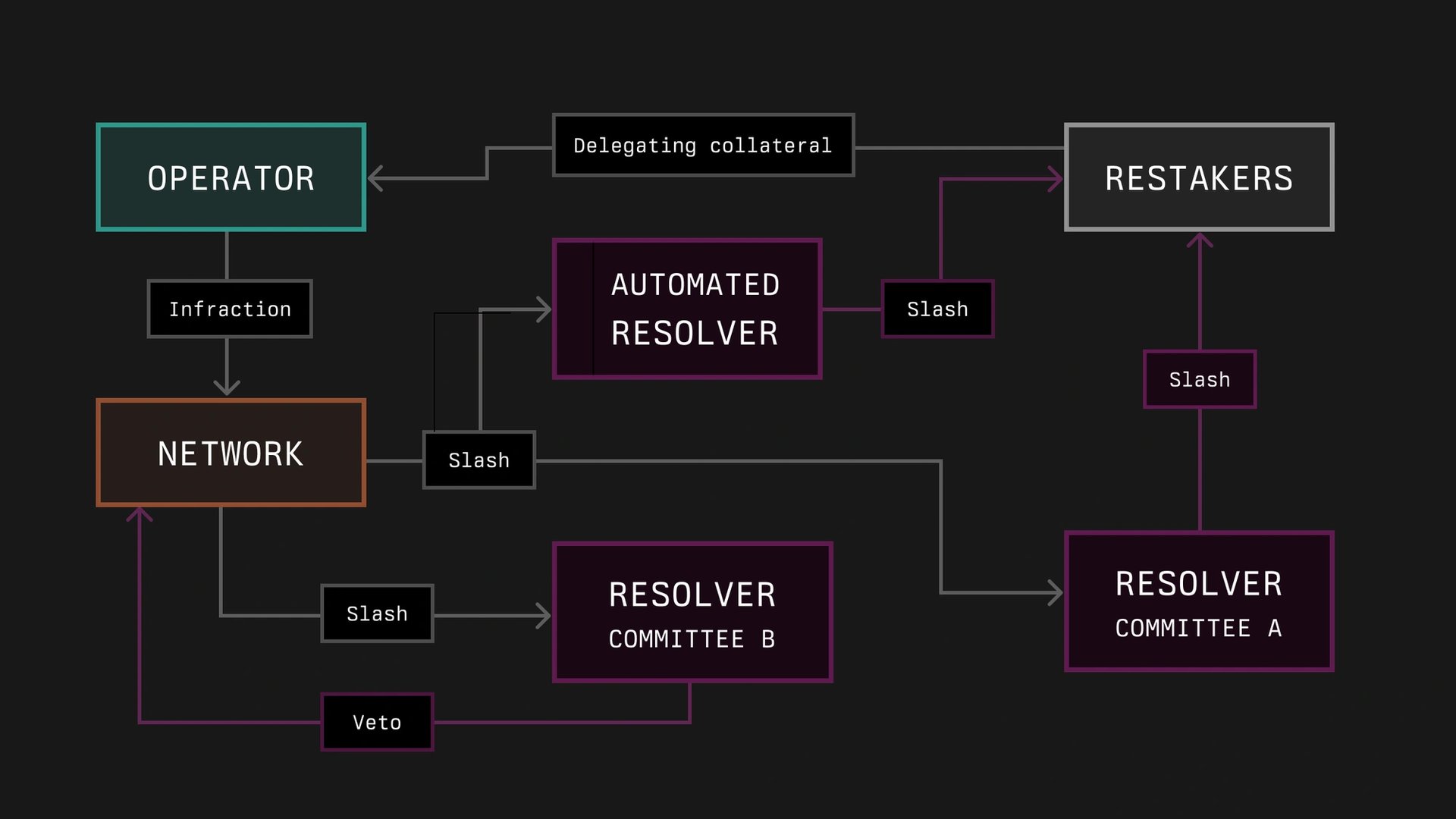
Symbiotic seeks to reduce risks through immutable Ethereum contracts and improve capital efficiency with a multi-asset, network-agnostic design. The protocol comprises five components: Collateral for representing on-chain assets, Vaults for managing asset delegation, Operators for network infrastructure, Resolvers for handling slashing penalties, and Networks for establishing their security methods.[1][2][3][4]

Products
Collateral
In Symbiotic, Collateral refers to assets used for network security that can be held outside the protocol, such as in DeFi positions. These assets are represented as ERC-20 tokens with functionalities to manage slashing incidents if required. Collateral tokens are deposited into vaults, which aim to allocate them to operators. Vaults set terms for acceptable collateral and slashing mechanisms, and networks must agree to these terms to participate.
Default Collateral is a basic version of collateral tokens, functioning as a wrapper over ERC-20 tokens with optional slashing history features. This implementation aims to provide additional management capabilities.[5]
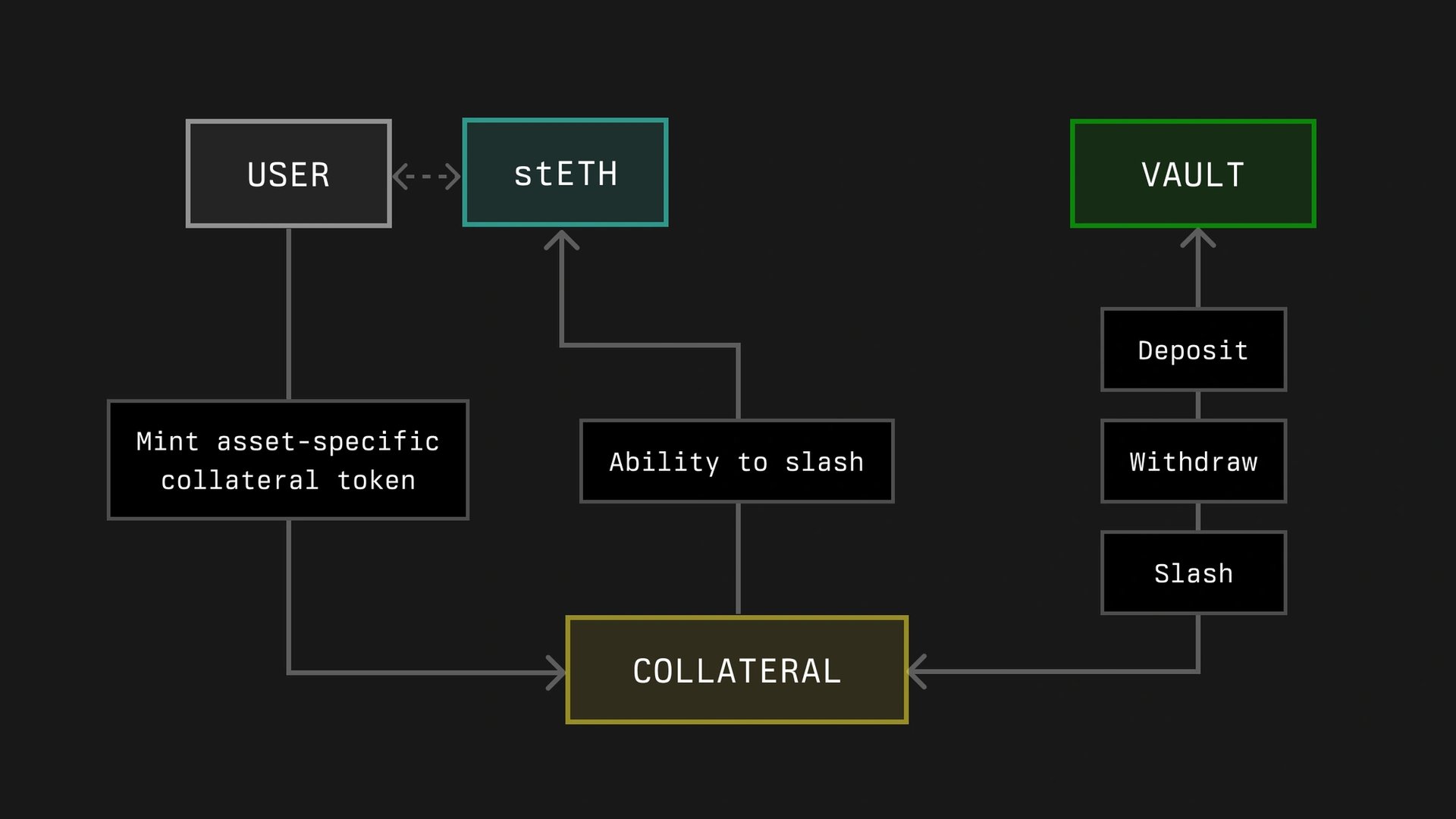
Vaults
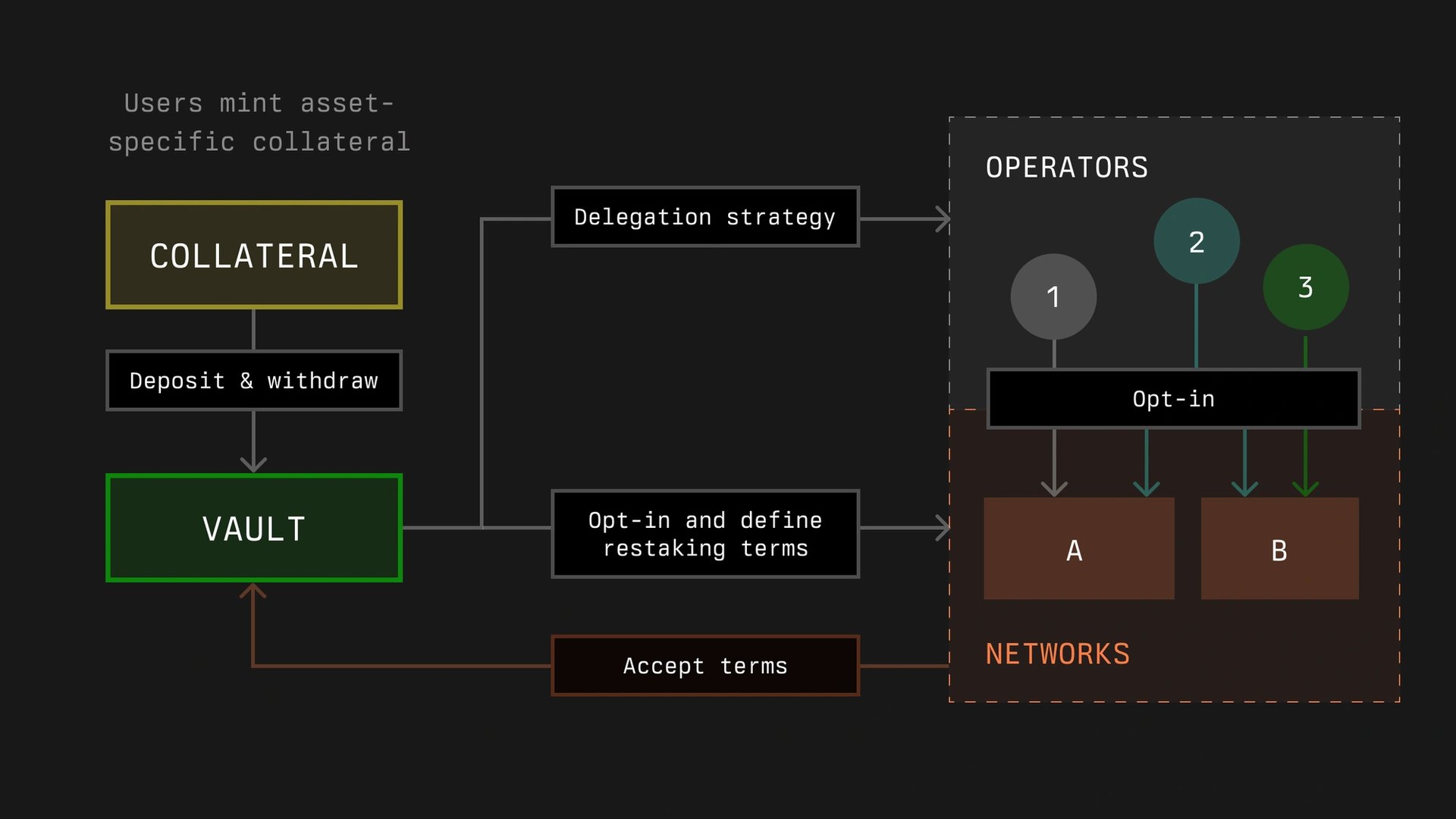
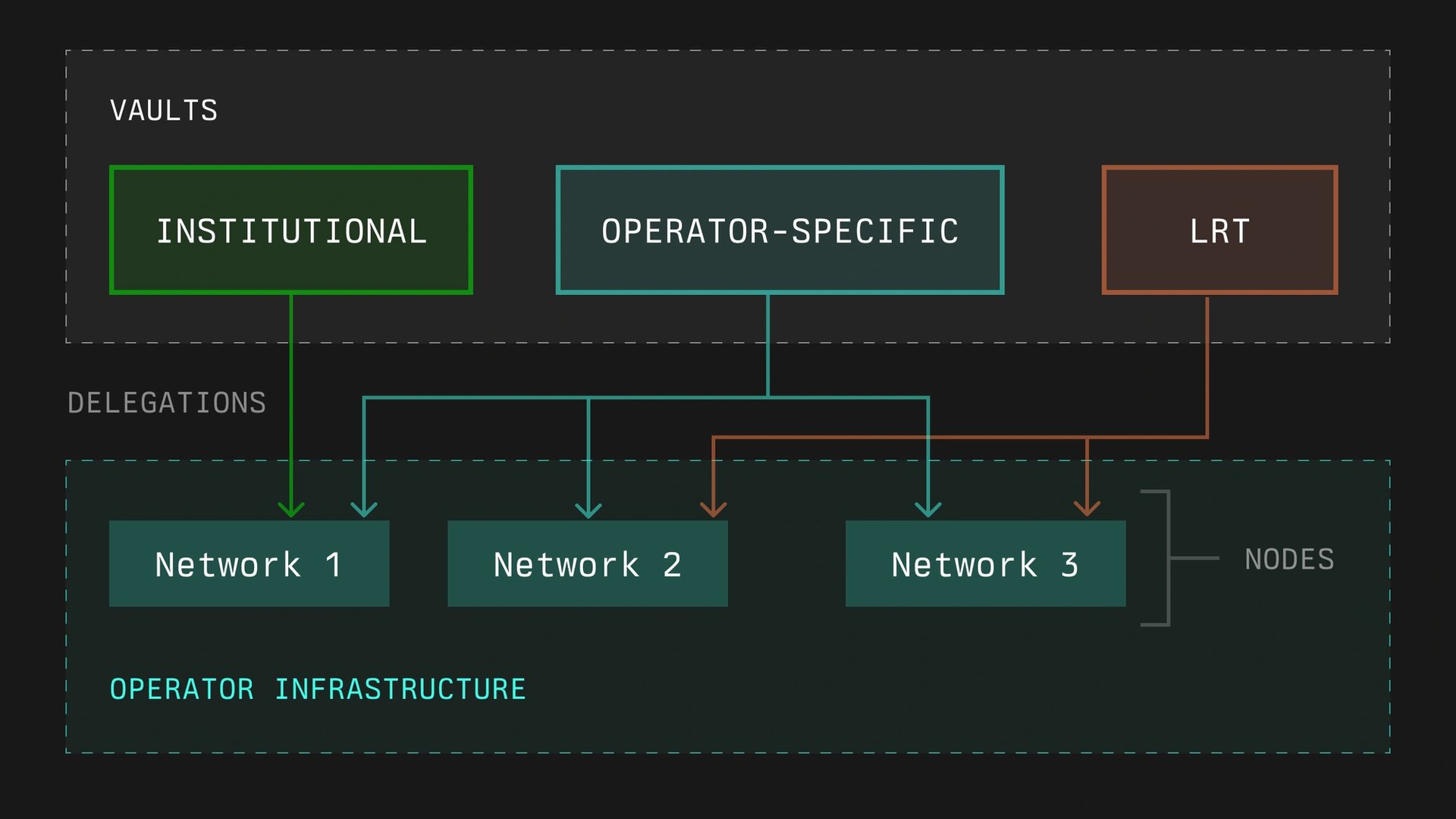
Vaults in the Symbiotic protocol aim to manage the delegation and restaking of collateral. They handle deposits, withdrawals, slashing, and the distribution of rewards to depositors. Vaults can be configured to be immutable or adjustable, and support various use cases such as operator-specific or multi-operator arrangements.
Each vault operates with a predefined ERC-20 collateral token and includes modules for accounting, slashing, and delegation. The protocol allows for slashing to be executed immediately or through a veto process, based on network specifications. The design of vaults seeks to provide both flexibility and security in handling collateral and rewards.[6]
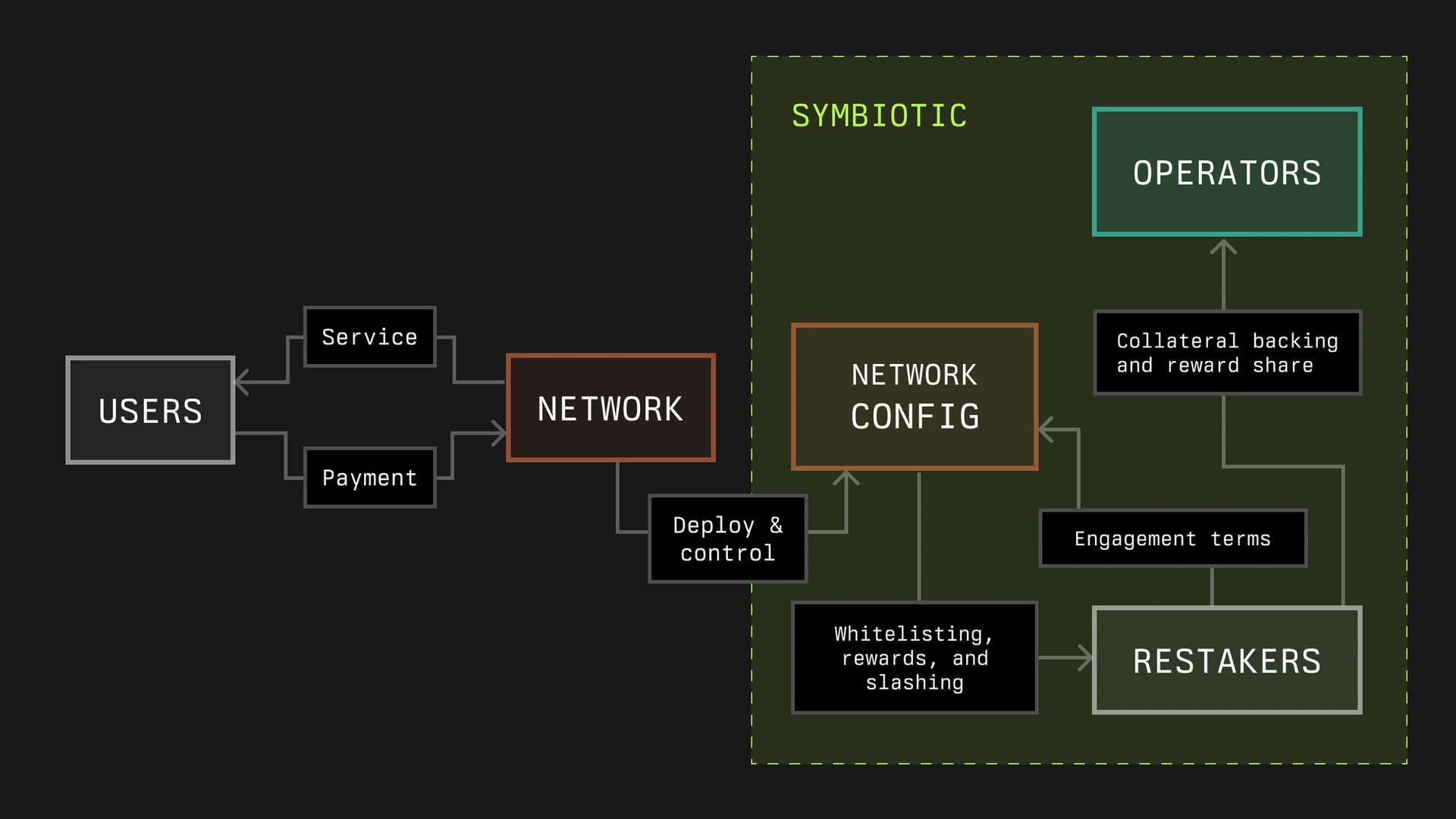
Networks
In the Symbiotic framework, networks represent decentralized systems that require security and economic backing, which they aim to acquire through Symbiotic. These networks are identified by an address and a middleware contract, which includes slashing logic, and operate within defined periods called epochs. Networks can establish rules and limits for stake allocation through a vault.
Slashing may be executed immediately or through a veto process, depending on the opt-in status of the operator and predefined limits. The amount slashed can be adjusted due to cross-slashing or veto procedures.
Rewards for operators and stakers are intended to be distributed through mechanisms such as off-chain calculations or on-chain methods, based on data from operator registrations and staking information.[7]
Operators
Operators manage infrastructure for decentralized networks and are registered in the OperatorRegistry. The protocol aims to facilitate the allocation of stakes from various sources through vaults, allowing a single node to support multiple networks.
Operators need to opt into networks and vaults to receive stakes, which are distributed based on defined limits. Networks independently determine operator inclusion based on criteria such as reputation and stake amount.
Once operators opt in, their stakes are active and subject to potential slashing. The slashing process is governed by the protocol's module, which includes optional timelocks to enhance security.[8]
Resolvers
Resolvers in Symbiotic are designed to manage slashing incidents by either approving or rejecting them. They can be either contracts or entities and may be utilized across different networks. The choice of resolvers is determined by agreements between networks and vaults. Vaults can employ various resolvers or none at all, including decentralized dispute resolution systems such as UMA or Kleros.
Resolvers process slashing requests from the slasher module of a vault. They have a defined period to either veto or accept a request. If no action is taken, the request is automatically considered accepted.[9]
Funding
Symbiotic has raised $5.8 million in seed funding, led by Paradigm and cyberFund. Paradigm is known for its investments in various crypto projects.[3][10]
Partners
Symbiotic established partnerships with several companies for its launch:
- Ethena
- LayerZero
- bolt
- Hyperlane
- Marlin
- Fairblock
- adri
- oio
- Drosera
- Blockless
- Rollkit
- Cycle
- Aizel Network
- stork
- Mind Network
- dopp[10]

See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
