Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Cosmos (ATOM)
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Cosmos (ATOM)
Cosmos (ATOM) is an open-source interchain network developed by Tendermint. It allows different blockchains, called zones, to communicate and exchange data, all connected by the Cosmos Hub which is powered by the Atom token. The end goal of Cosmos is to create an “Internet of Blockchains, a network of blockchains able to communicate with each other in a decentralized way”. [5]
Overview
History
In 2014, Jae Kwon established Tendermint, the founding team of the Cosmos ecosystem, by being the pioneer in applying Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) in a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) context. The project aimed to address the speed, scalability, and environmental issues related to Proof-of-Work (PoW). Later, Ethan Buchman joined the project and together they developed the Cosmos Software Development kit (SDK) to lower the barrier to entry for blockchain development and build a decentralized network of individual blockchains able to communicate with each other. Cosmos aims to solve the problems of sovereignty, scalability, and sustainability while providing an interoperability solution for connecting layer 1 blockchains. [1][2][3]
In 2016, the first Cosmos whitepaper was published, and during the following year, the project was able to raise around $16.8 M in funds. The Cosmos Network architecture was built and early prototypes were developed. Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) was later introduced in 2018, and since then, the network has continued to gain traction with projects utilizing the Cosmos SDK.[3]
Hub Theta, an upgrade to the Cosmos network, went live on April 13, 2022. This upgrade introduces interchain accounts, allowing users to permit an application running on one blockchain to execute on another one. It also includes updated versions of Cosmos SDK and of the IBC, which let users complete transactions in a single action.[4]
Architecture
The Cosmos network is composed of three layers: the application layer, the consensus layer, and the networking layer. Cosmos incorporates Tendermint BFT in the consensus and networking layers and utilizes Cosmos SDK as a tool in the application layer. The network utilizes open-source tools to connect these layers together and provide a safe environment for the development of dApps.[5]
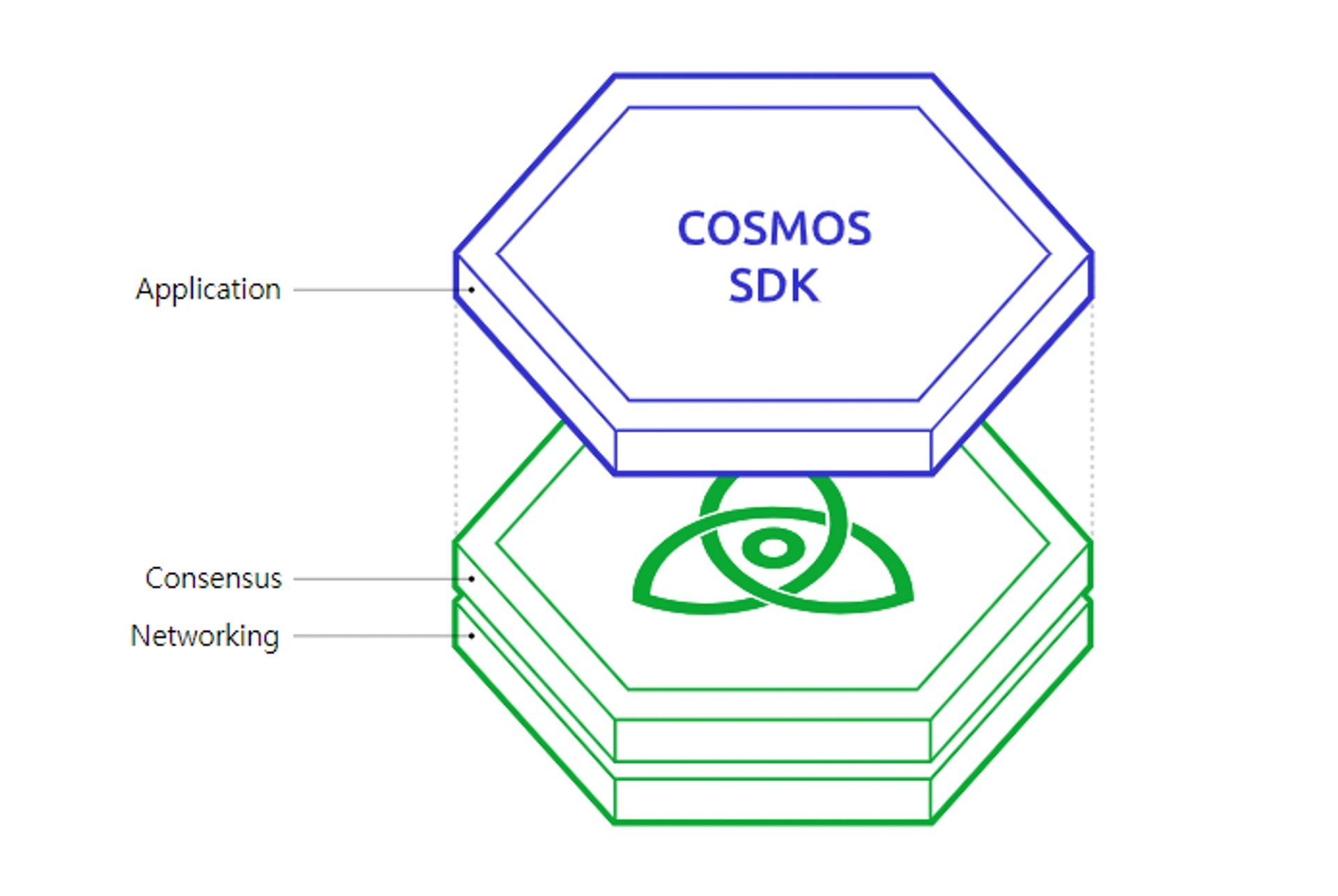
Tendermint Bizantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
Cosmos SDK tools use by default Tendermint BFT, a Proof-of-Stake consensus protocol that allows developers to build blockchains without having to code them from scratch, as the networking and consensus layers are packaged into a single generic engine.[2] It utilizes the application blockchain interface protocol to connect to applications, validate transactions, and execute blocks.
Tendermint BFT is connected to the application through a socket protocol called the Application Blockchain Interface (ABCI), where any programming language can be utilized, thus allowing developers to solely focus on the building of applications.[6]
In Tendermint, nodes can have a non-negative or positive amount of voting power. In the last case, these nodes are called validators and can participate in the consensus protocol by voting on the next block. Validators’ voting powers can either be determined at genesis or changed afterward.[6]
The protocol requires a set of validators identified by their public key, who will aim to vote for consensus on each block. The proposer for a round is chosen in proportion to their voting power. [6]
Cosmos SDK
The Cosmos SDK is a generalized framework that facilitates the building of applications on top of Tendermint BFT. It is based on the principles of modularity and capabilities-based security.
Cosmos SDK gives the developer the freedom of utilizing their language of choice for the building of a dApp. Among these options, CosmWasm is a module that allows the execution of the WebAssembly bytecode.
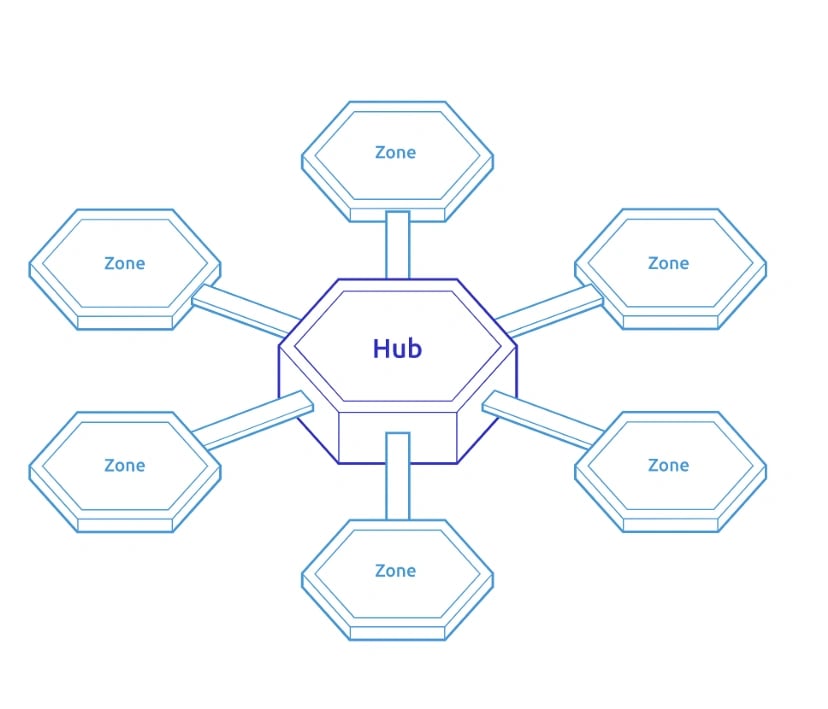
Cosmos Hub
The Cosmos Hub is the central blockchain of the Cosmos ecosystem. It provides a multi-asset distributed ledger where tokens are held. Tokens are moved from one zone to another in a special IBC packet called a “coin packet”, where transactions are executed by the sender, hub, and receiver blockchains.[6]
Inter-blockchain Communication (IBC)
IBC is a protocol that facilitates the transmission of messages and exchange of data between heterogeneous chains and connects them to the Cosmos Hub.
ATOM
ATOM is the main token utilized in the Cosmos Hub. Holders can delegate their ATOM to validators who contribute to the security and governance of the blockchain, and in return, they can earn ATOM as a reward through Proof-of-Stake.
Tokenomics
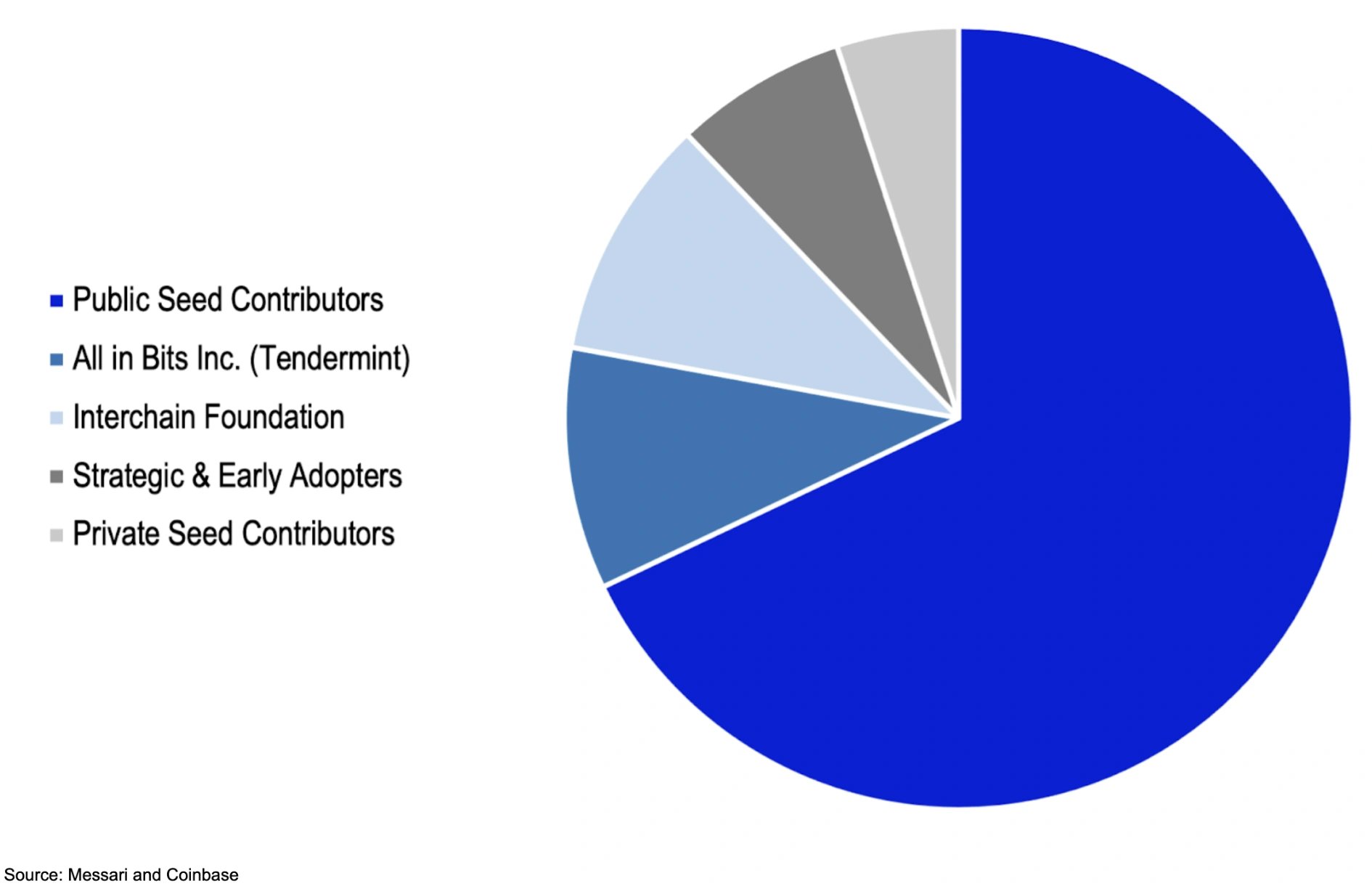
ATOM has a total supply of 260,906,513 tokens. Instead of being mined, they are earned through staking. In 2017, two private sales and one public sale took place, which raised a total of $16 million. 80% of the token distribution was allocated to investors, and the remaining amount was split between the companies All In Bits and the Interchain Foundation.[7]
The target staked ratio is two-thirds of the total token supply. In case of a larger quantity of ATOM being staked, issuance will decrease accordingly in order to guarantee the availability of liquidity. In the opposite case, where the ratio falls below the expected number, issuance will be increased until the ratio is matched.[8]
Fees
All fees generated due to transactions are sent to the distribution module to be split afterwards among the Community Pool, delegators, and validators.
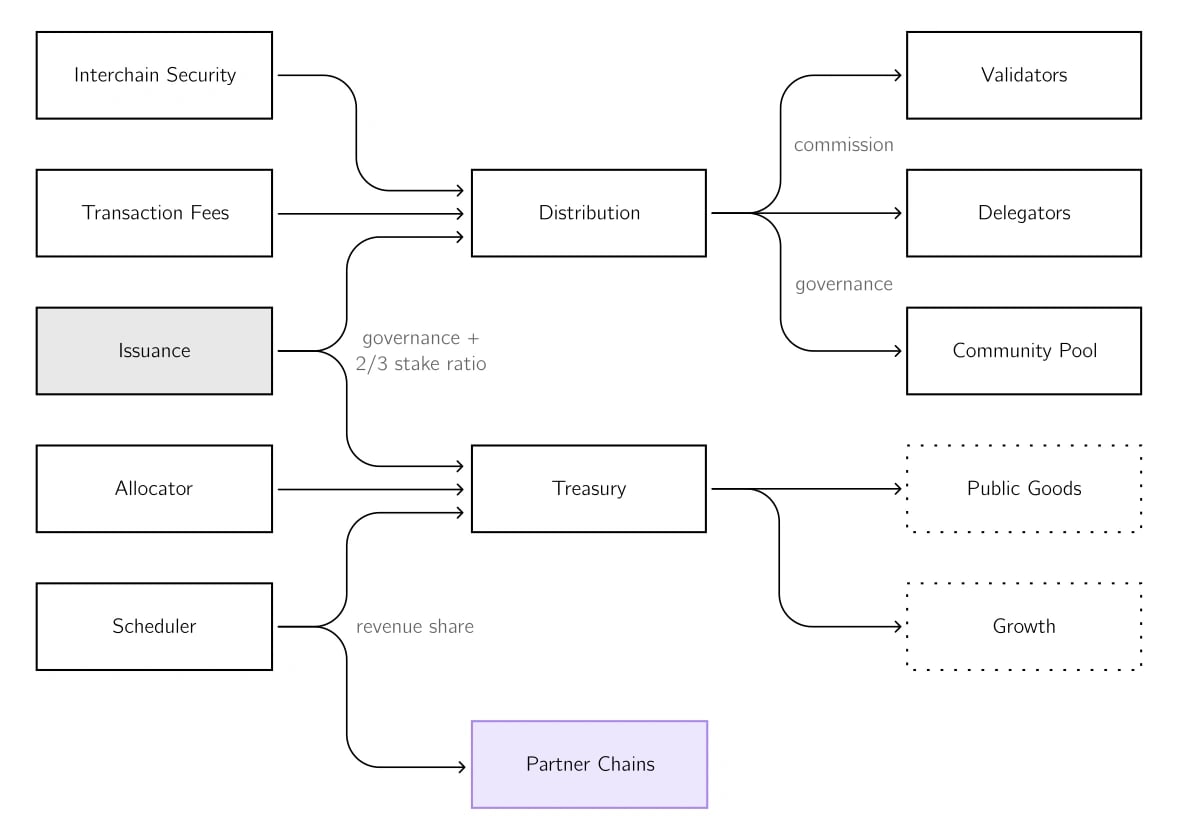
Interchain Security is in charge of incentivizing validators and delegators by maintaining the two-thirds staking ratio. A global fee model that begins with a whitelist of accepted tokens along with corresponding minimums will also be implemented. This structure will ultimately shift to a single ATOM floor fee that adjusts automatically based on the demand for using the network.[8]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
