Karak
Karak is an EVM-compatible Layer 2 blockchain focusing on financial security while emphasizing efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. It combines risk management, restaking, and AI to allow developers to create secure and efficient blockchain applications from the outset. Additionally, Karak aims to extend its safety and security paradigm to other blockchains through an upcoming interoperability mechanism. The co-founders of Karak are Raouf Ben-Har and Drew Patel. [1][4]
Overview
Karak is a universal restaking layer that facilitates crypto-economic security for various assets. It offers developers a secure platform to create innovative infrastructure designs effortlessly. It provides protocols with access to secure trust networks from the outset, reducing the hurdle of securing new protocols. By eliminating the need for protocols to incentivize their validator sets with highly dilutive reward mechanisms, Karak makes initiating security more scalable, accessible, and cost-effective. [1]
Users can repurpose their staked assets on Karak to extend the security of Ethereum and other trust networks to additional applications. Through a Distributed Secure Service (DSS) on Karak, stakers can opt-in to grant additional enforcement rights on their assets, imposing slashing conditions to ensure participant integrity and application security. [1]
As a marketplace, Karak enables developers to incentivize validators to allocate restaked assets to secure their services. This approach replaces the issuance of highly inflationary tokens by applications, reducing the financial and temporal investment required to establish a new trust network. Moreover, Karak's universal restaking facilitates enhanced bootstrapping and composability across networks by standardizing capital requirements despite varying staking parameters. [1]
Features
Multiasset Restaking
Karak introduces multi-asset restaking, a novel feature in crypto-economic security enabling users to restake assets like Ethereum, liquid staking tokens, stablecoins, and others to earn rewards. This innovation enhances security for diverse applications, protocols, and Distributed Secure Services (DSS) across the Ethereum ecosystem and beyond. [1]
Universal Restaking
Karak utilizes the concept of universal restaking, simplifying the process of initiating security and network interoperability while ensuring that secure restaking infrastructure is accessible globally. This approach enables developers to prioritize innovation and product development, reducing the emphasis on bootstrapping security measures. [1]
Turnkey Development
Karak allows distinctive systems to access secure trust networks immediately, reducing the difficulty of securing new protocols. It removes the requirement for protocols to incentivize their validator sets with overly dilutive reward systems, thus enhancing the scalability, accessibility, and affordability of initiating security measures. [1]
Restaking
Users can use several methods for restaking, such as: [1]
- Liquid Staking/Restaking allows users to restake by depositing their Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) or Liquid Restaking Tokens (LRTs) into Karak smart contracts. Validators can then take these tokens, which have already been staked in protocols like Lido, Rocket Pool, Mantle, and Etherfi, and restake them on Karak.
- Stablecoins: Users can restake their stablecoins by depositing them into Karak smart contracts, offering a novel method for participation. Validators can also restake stablecoins already staked in protocols like sDAI on Karak.
Ecosystem
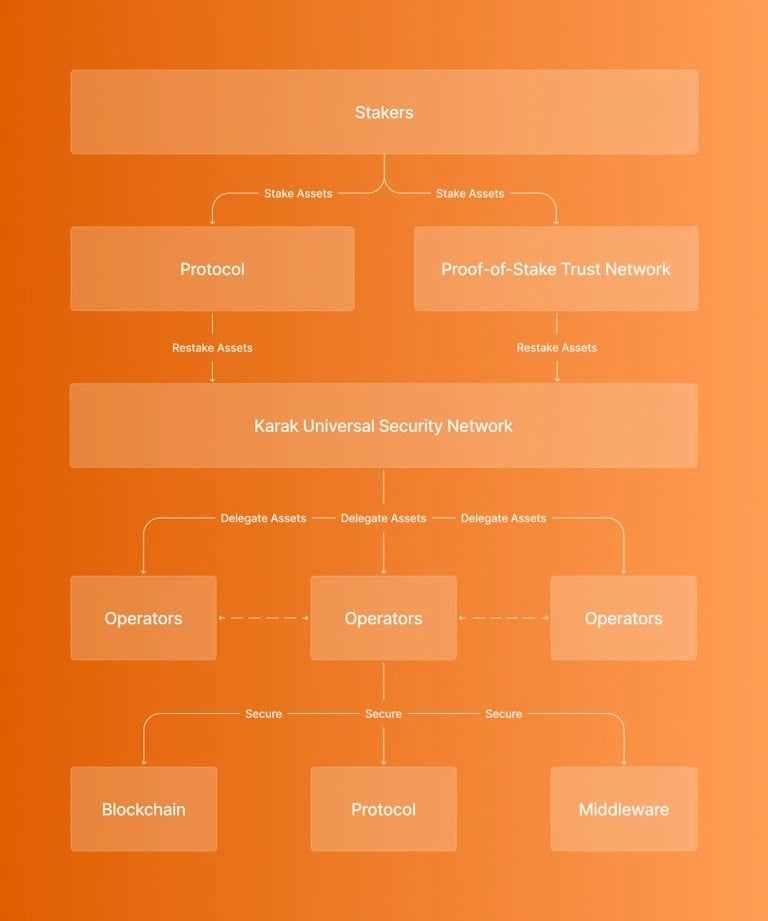
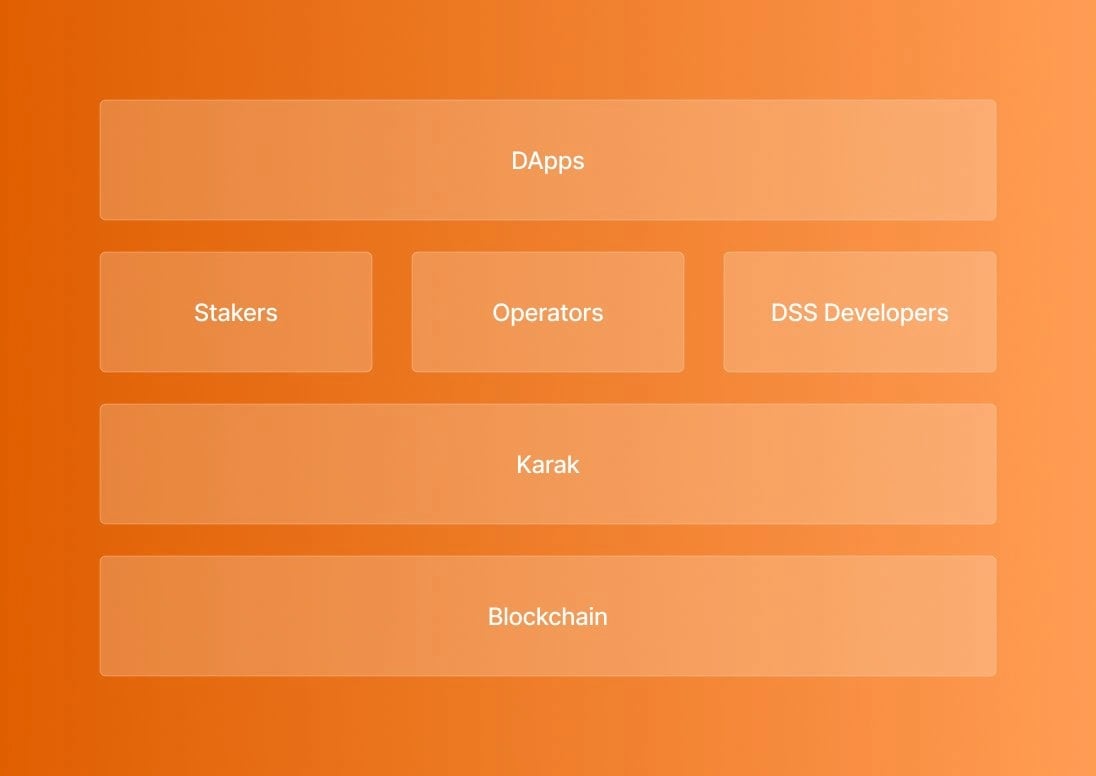
Karak's architecture consists of several key components: [1]
- Restakers contribute to universal security across Ethereum and other blockchains by staking assets in exchange for rewards. These restakers are crucial in bolstering security measures and making secure restaking infrastructure accessible to everyone.
- Distributed Secure Services (DSS) utilize restaked assets to enhance security while reducing operational expenses. These services are vital for ensuring the integrity and reliability of various blockchain applications and protocols. Several DSS initiatives will be introduced in the coming weeks, including core services developed by Karak contributors.
- Chains or rollups leverage the services provided by distributed secure services to enhance their security and functionality. For example, K2, a risk management L2 platform built on Karak, utilizes DSS services to strengthen security measures. K2 is a cost-effective sandbox for DSS development, testing, and protocol upgrades before deploying services on the L1. Additionally, K2 fosters greater decentralization within the ecosystem by enabling more validators to validate DSSs through custom precompiles.
- Operators, whether individuals or organizations play a crucial role in validating and securing distributed secure services (DSS). They ensure the smooth operation of DSS initiatives and contribute to the overall security and reliability of the blockchain network.
Within the Karak Ecosystem, there are various integrated tools and services for users to use, including: [3]
- Karak Bridge: Enables smooth asset transfers across Ethereum, Arbitrum, Optimism, and Karak.
- Subsea: A marketplace for risk management that detects digital asset risks automatically and impartially.
- SlashProof: Offers protection for staked and restaked assets through zero-knowledge proofs.
- Watchtower: A security platform that conducts realistic market simulations to stress test applications.
- Kekswap: A decentralized exchange that provides users with optimal trading experiences and prices.
Investors
- Coinbase
- Mubadala Capital
- Pantera Capital
- Framework Ventures
- Bain Capital Ventures
- Lightspeed
- Digital Currency Group
- Proof Group
- Nima Capital
- Naval Ravikant
- Joey Krug
- Napoleon Ta
- Anthony Pompliano
- Nikil Viswanathan
- Santiago Roel Santos
- Joe Lau
- Noah Jessop[4]

