Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Whisper
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Whisper
Whisper is a protocol for secure, peer-to-peer messaging on the Ethereum network. Whisper is designed to provide a secure and private communication channel for decentralized applications (dApps) and users on the Ethereum network.[1][5]
Overview
Whisper is a protocol for building decentralized apps (Dapps) on the distributed ledger system supporting blockchain technology that allows messaging between DApps. It provides a simple API that we can use to send an encrypted message through the Ethereum blockchain and receive and decrypted messages with the hash key.
Whisper is being built as a protocol, meaning that it lays the foundation for higher-level implementations, DApps, built on it, with different variations, using different features of the protocol, and different settings. Whisper protocol implementation builds on top of the RLPx transport protocol that is internally used by Ethereum for communication between nodes. [5]
Whisper supports the Geth and Parity clients. It can be used for DApps publish-subscribe coordination signaling and building secure, untraceable decentralized communication.[2][6]
Whisper conceals the content of messages and the identities of senders and receivers from observers. Messages on Whisper have a time-to-live (TTLT) timer, which means they expire after a certain period. The system relies on a double layer of data encryption.[4]
The whole concept of the Ethereum Whisper communication protocol revolves around three objectives:[3]
- providing users with a flexible system
- launching a secure communication channel on Ethereum
- most importantly, guaranteeing the users’ anonymity online.
Initially, Whisper was developed as part of Ethereum's broader goals to enable private and secure messaging between decentralized applications (DApps). However, its adoption has slowed over time, and it has mostly remained in a proof-of-concept phase rather than achieving widespread implementation. Whisper’s full functionality is still available, although many developers now prefer alternative communication protocols.
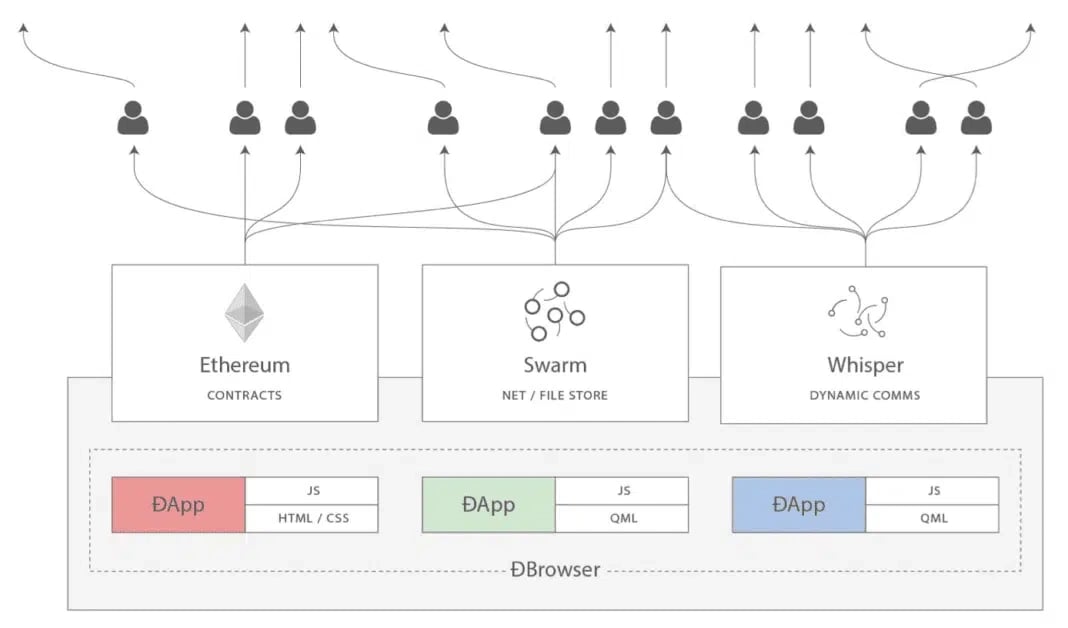
Whisper as one of Ethereum's 3 pillars for Web 3.0
Most recently Gavin Wood published ‘Dapps: What Web 3.0 Looks Like’. Here we are introduced to the Internet as a “zero-trust interaction system” made possible by a decentralized and encrypted information publication system, a pseudonymous low-level messaging system and a consensus engine.[7]
In the Ethereum ecosystem, Web 3.0 is implemented in the form of three pillars, of which one is the Ethereum Whisper protocol, which is designed to bring about the emergence of DApps, and by extension Web 3.0, by acting as a secure and decentralized messaging protocol.
- The first pillar is smart contract technology, which is run on the Ethereum blockchain as a trusted immutable backend. With smart contracts, the code of the decentralized application is executed on top of a trusted P2P protocol, instead of a web server.
- The second pillar, decentralized storage, can be found in the form of Swarm. This allows the off-chain parts of DApps, such as web interfaces and larger pieces of data, to be stored in a decentralized manner, eliminating the need for centralized file storage or databases.
- The third element of the Web 3.0 vision involves privacy-focused secure messaging. There are a number of situations in which DApps need to communicate through a message bus outside the context of blockchain transactions. Message buses allow applications or users to interchange messages point-to-point or in a broadcast fashion. Traditionally, this has been achieved by centralized message servers. Reasons for DApps to keep communication off-chain include:
- Privacy
- Temporary limits for the validity of a message (a time-to-live property)
- The cost of on-chain transactions
In Ethereum, the Whisper protocol is designed to take on the role of a secure off-chain message bus.[5]
Technology
The Whisper protocol uses a combination of public key cryptography and a distributed hash table (DHT) to ensure that messages are both secure and private. Each user on the network is assigned a unique public key, which is used to encrypt messages sent to them. The DHT is used to securely distribute and store these encrypted messages, allowing for peer-to-peer communication without the need for a centralized server.
One of the key features of Whisper is its support for “topics” or “channels,” which allow users to subscribe to specific types of messages or conversations. This makes it easy for dApps and users to create and participate in specific communities or groups on the Ethereum network.
Whisper is also designed to be lightweight and efficient, making it well-suited for use on mobile devices and other resource-constrained platforms. This makes it an attractive solution for dApps and other projects that need to provide secure, private messaging capabilities to users on the go.[1]
The system relies on a double layer of data encryption:[3]
- Symmetric encryption allows transmitting one-to-many communications using a single encryption and decryption key. The recipients of a message can decrypt the messages sent to them.
- Asymmetric encryption employs public keys for encryption and private keys for decryption. When communicating with another person, the system uses this type of encryption.
Whisper uses the ssh protocol string of devp2p. When sending an encrypted message, the message content can be encrypted by default either asymmetrically or symmetrically.
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public key cryptography, uses public and private keys to encrypt and decrypt data. One key is public and it is shared with everyone. The other is a private key; only the owner can see or access private key information. When encrypting the Whisper message, it uses the standard Elliptic Curve Integrated Encryption Scheme with the SECP-256k1 public key to encrypt a message; the other key is used for decryption. Symmetric cryptography (also known as the secret key), on the other hand, uses the hash key with the AES GCM algorithm with a random 96-bit nonce for both encryption and decryption. It typically facilitates one-to-many messages. The sender and receiver use the same symmetric key to encrypt and decrypt the message.[2]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
