Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Gwei
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Gwei
Gwei, is a small denomination of the cryptocurrency Ether (ETH), the native currency of the Ethereum blockchain. Gwei is short for gigawei and is also called a nanoether, or simply nano, to denote the ninth power of the fractional ETH. This term is also widely used talking about gas, and the Ethereum network's transaction fees.[1][4]
[5]
Overview
Gwei is short for “Giga Wei”, which is equivalent to one quintillion weis of Ethereum, 0.000000001 ETH. A gwei is also called nanoether, and it is one billionth of one ETH. Gwei is the most commonly used ether unit because it is used to denote gas. Gas is the term used in the Ethereum network for transaction power. Gas fees are payments made by users to compensate the miners and validators for the computing energy required to process and validate transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.[6]
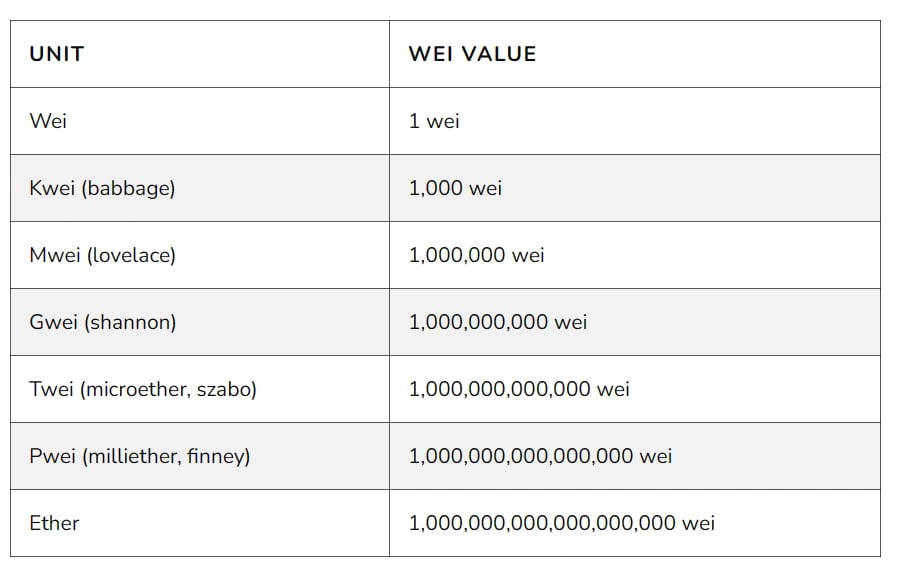
1 Gwei is equal to 1 billion (1,000,000,000) Wei, where Wei is the smallest denomination of Ether. As Ether's value can vary significantly, using Gwei as a unit of measurement for gas costs helps to standardize transaction fees and network usage. If a transaction is said to have a gas price of 20 Gwei, it means that for each computational step or operation in that transaction, the sender is willing to pay 20 billion Wei (or 0.00000002 ETH) as a fee to miners for processing the transaction. The gas price is a factor in determining the priority of a transaction, higher gas prices often result in faster transaction confirmation times. In Ethereum network slang, Gwei is also sometimes referred to as shannon, after American mathematician and computer scientist Claude E. Shannon. Shannon is credited with laying the foundation for information theory.[6][7][8]
Denominations of Ether
Wei (Wei) - Dai Wei formulated the concepts of all modern cryptocurrencies, and is best known as the creator of the predecessor to Bitcoin, B-money.
Kwei (Babbage) is named after Charles Babbage (1791-1871), an English mathematician and mechanical engineer who is considered the father of the computer. Babbage’s designs for his analytical engine, a mechanic computer, would go on to inspire modern computer scientists. Modern recreations of his designs have been successful in proving his idea would have worked if it was feasible to build.
Mwei (Lovelace) is named after Ada Lovelace (1815-1852), a brilliant mathematician and daughter of the poet Lord Byron, collaborated with Babbage. She wrote what many consider the first computer program which would have derived Bernoulli numbers had the engine ever been built. She also had the idea of applying punchcards from weaving looms to input a sequence of instructions into Babbage’s analytical engine.
Gwei (Shannon) is named after Claude Shannon (1916-2001), an American mathematician and electrical engineer known as “the father of information theory.” Shannon also designed early digital circuits which could solve Boolean algebra. His work laid the groundwork for the digital computers and networks we use today.
Twei (Szabo) is named after Nick Szabo, a computer scientist, legal scholar, and cryptographer known for his pioneering research in digital contracts and digital currency. Szabo designed bit gold, a decentralized digital currency also said to have influenced Satoshi Nakamoto’s design of Bitcoin. Szabo proposed and coined the term “smart contracts.
Pwei (Finney) is named after Hal Finney (1956-2014), a cryptographic activist, developer for the PGP Corporation, creator of reusable proof of work, and early Bitcoin contributor. Finney was allegedly the first recipient of a Bitcoin transaction, sent from Satoshi Nakamoto himself.
Ether (Buterin) is named after Vitalik Buterin the creator of Ethereum.[2][3]
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)