Subscribe to wiki
Share wiki
Bookmark
Movement Network
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
0%
Movement Network
Movement Network is a secure and scalable network of Move-based chains secured by Ethereum. It is designed to provide safer execution environments for blockchain applications through the Move programming language and virtual machine (MoveVM). [3]
Overview
Movement Network is a blockchain framework that utilizes the Move programming language and virtual machine to support modular, application-specific chains. It incorporates Move Rollups, which enable interoperability between different blockchain environments, and is structured around the Move Stack, a framework for creating customizable Move-based networks. The system integrates Ethereum’s security model while leveraging Move’s resource-oriented programming to enhance transaction handling and contract execution.
Designed to address security and performance limitations in existing blockchain infrastructure, Movement Network employs MoveVM’s parallel execution capabilities to improve processing efficiency. Its architecture reduces common smart contract vulnerabilities while maintaining compatibility with Ethereum-based applications. The network is structured to facilitate secure and efficient blockchain development by emphasizing transaction finality and interoperability. [1] [2]
Technology Architecture

Move Programming Language
Move is a blockchain programming language designed for secure and efficient smart contract development, introducing resource-oriented programming to prevent common vulnerabilities. Unlike Solidity, Move treats assets as resources that cannot be duplicated or lost, ensuring safe management through ownership rules. It supports modules for reusable code, generics for flexibility, and pattern matching for efficiency. Move includes formal verification tools like the Move Prover and a bytecode verifier to prevent malicious code execution. These features make Move a robust and secure language for Web3 development, minimizing risks like re-entrancy attacks while improving productivity.
Move's features include resource-oriented programming, where digital assets are treated as unique resources that can only be moved, not copied or discarded. It also incorporates formal verification through the Move Prover, a strong typing system to reduce errors, and linear types that enforce single-use resources to prevent double-spending. [5] [7]
Move Virtual Machine (MoveVM)
MoveVM is a blockchain virtual machine that utilizes the Move programming language, designed to enhance transaction integrity and security through its resource-oriented architecture. Unlike traditional blockchain systems, which treat assets as balances within accounts, MoveVM views digital assets as unique, indivisible entities, preventing duplication or unauthorized destruction. This design ensures greater security and reliability, addressing risks such as fraud and errors in asset management.
In addition to its resource-oriented framework, MoveVM incorporates several features to improve blockchain performance and security. It includes a bytecode verification process that scrutinizes executable code to meet strict safety standards, reducing vulnerabilities. MoveVM also introduces a Transaction-as-Script model, which allows scripts to be embedded directly within transactions, optimizing resource usage and increasing efficiency. Furthermore, it supports parallel transaction processing through its BlockSTM system, significantly boosting transaction throughput. [2] [8]
Move Executor
The Move Executor is the core execution module of Move-based chains, supporting both MoveVM and EVM bytecode on the same network. Transactions are categorized as Move or EVM and routed to the corresponding interpreter—MoveVM or Geth. Each execution produces a change set, which is merged into global storage according to MoveVM rules. The module integrates with BlockSTM, MoveVM’s parallel execution engine, allowing for parallel EVM execution while maintaining EVM equivalence. This ensures that EVM bytecode behaves the same as on Ethereum L1 while benefiting from MoveVM’s efficiency and security. [2]
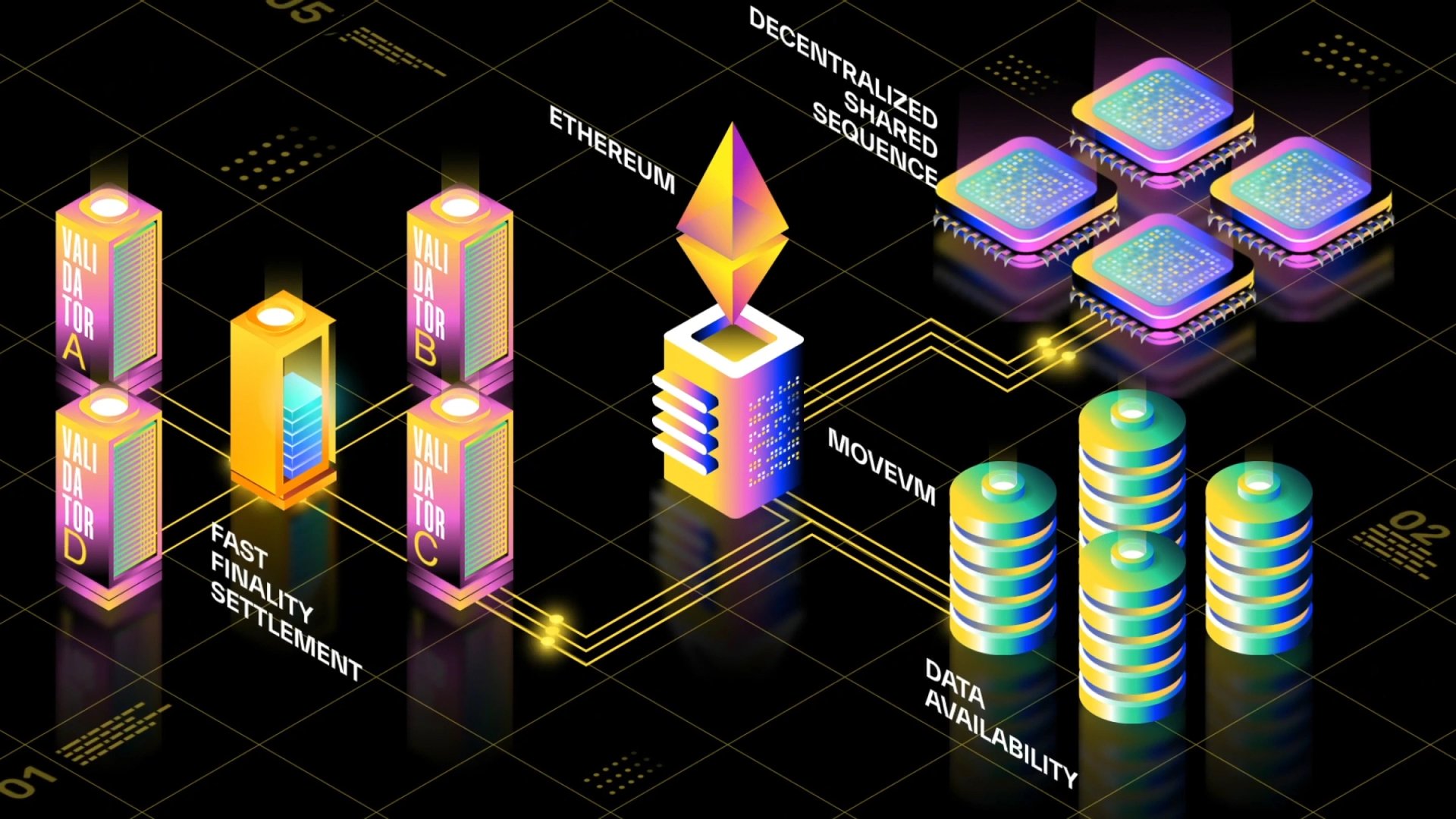
Fast Finality Settlement (FSS)
Fast Finality Settlement (FFS) is a staking-based settlement mechanism for Move Stack Chains that prioritizes fast finality while maintaining high crypto-economic security. It operates similarly to Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) system, requiring validators to stake assets and confirm state transitions. Validators risk slashing if they act maliciously, ensuring economic incentives for honest participation.
FFS contrasts with traditional Layer 2 rollups by providing near-instant settlement, unlike ZK-rollups, which rely on computationally expensive proofs, and optimistic rollups, which require a challenge period (often a week). By confirming transactions within seconds, FFS enhances interoperability and cross-chain interactions, where rapid settlement is critical.
While its security depends on the total stake of validators, a sufficiently large stake can approach Ethereum-level security. FFS can also be combined with rollup-based settlements in a dual-settlement approach, offering Ethereum security and fast finality guarantees. [1] [2]
Decentralized Shared Sequencer (DSS)
The Decentralized Shared Sequencer (DSS) in the Movement Network functions as a decentralized transaction sequencer, differing from centralized rollup sequencers by reducing single points of failure and improving censorship resistance. It uses a Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) consensus protocol to order transactions efficiently, maintaining security while offering fast confirmations. DSS enables interoperability across Move-based chains by providing a unified sequencing layer, facilitating cross-chain transactions and shared liquidity.
DSS operates using a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) mechanism, allowing multi-asset staking where participants can stake and receive rewards in different assets. While this approach increases flexibility, it introduces challenges such as asset price fluctuations and potential centralization risks if a small group gains control over staking power. To address this, a staking pool token model is proposed, where assets are staked in exchange for pool tokens, enabling rebalancing strategies to maintain security. Delegation further enhances economic security by allowing staking without requiring node operation. [2] [7]
MOVE
$MOVE is the utility token of the Movement Network, designed to support network security, transaction processing, and governance. Validators stake $MOVE to secure the network and earn staking rewards under the fast-finality settlement mechanism. Gas fees on the Movement Network L2 are paid in $MOVE, with a portion allocated for Ethereum settlement costs. Over time, governance will be decentralized, allowing token holders to propose and vote on network changes. As the native asset, $MOVE facilitates liquidity, collateralization, and payments within the ecosystem. [6]
Tokenomics
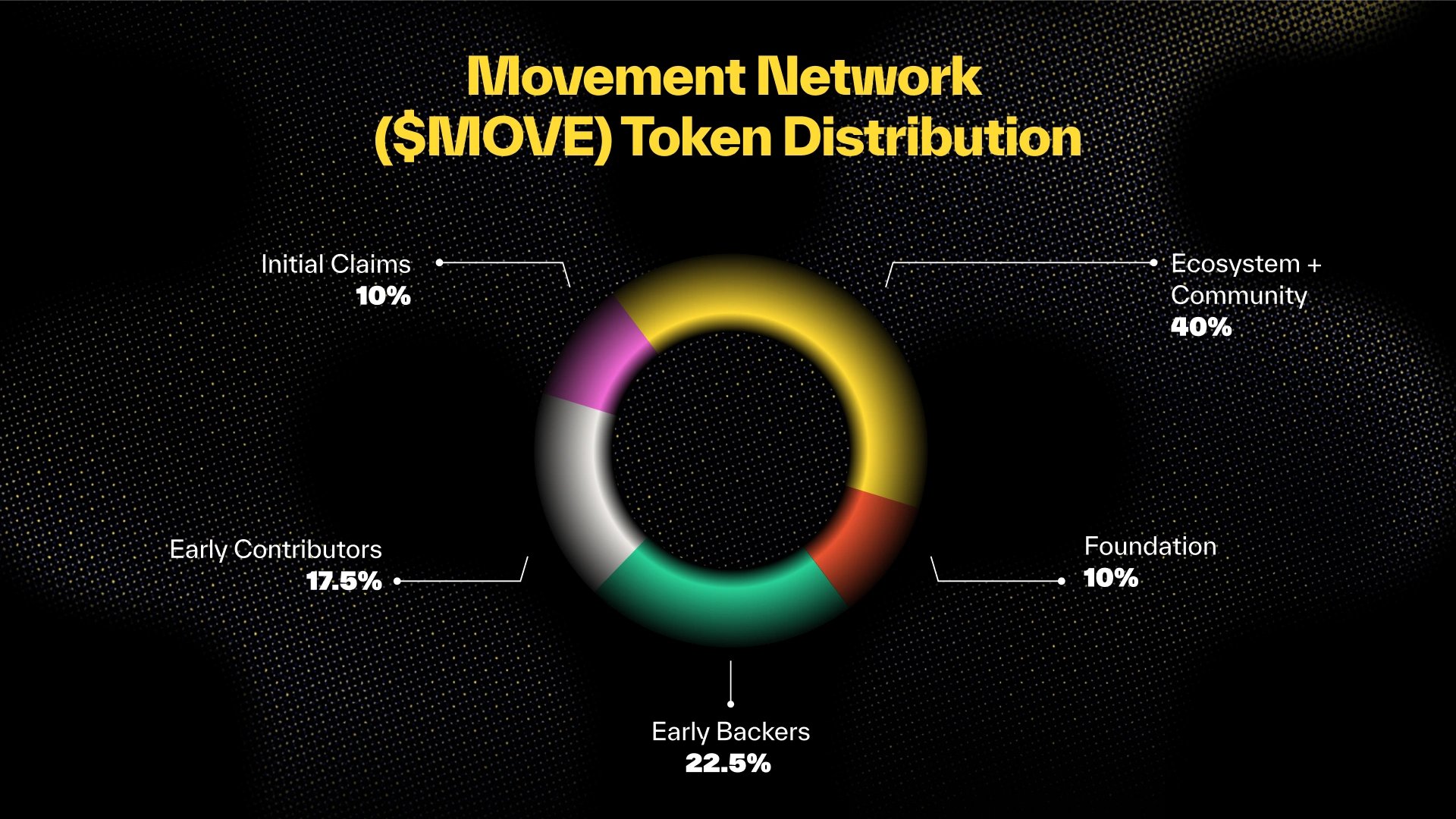
$MOVE has a maximum supply of 10B and has the following distribution: [6]
- Ecosystem/Community: 40%
- Early Backers: 22.5%
- Early Contributors: 17.5%
- Foundation: 10%
- Initial Claims: 10%
Partnerships
Turnkey
Flipside
Union
Gauntlet
Thala Lab
GAIMIN
Hyperlane
Interest Protocol
Colony Lab
Ultiverse
BENQI
Shogun Finance
GoGoPool
See something wrong?
The Agent Tokenization Platform (ATP):Build autonomous agents with the Agent Development Kit (ADK)
