Orbs
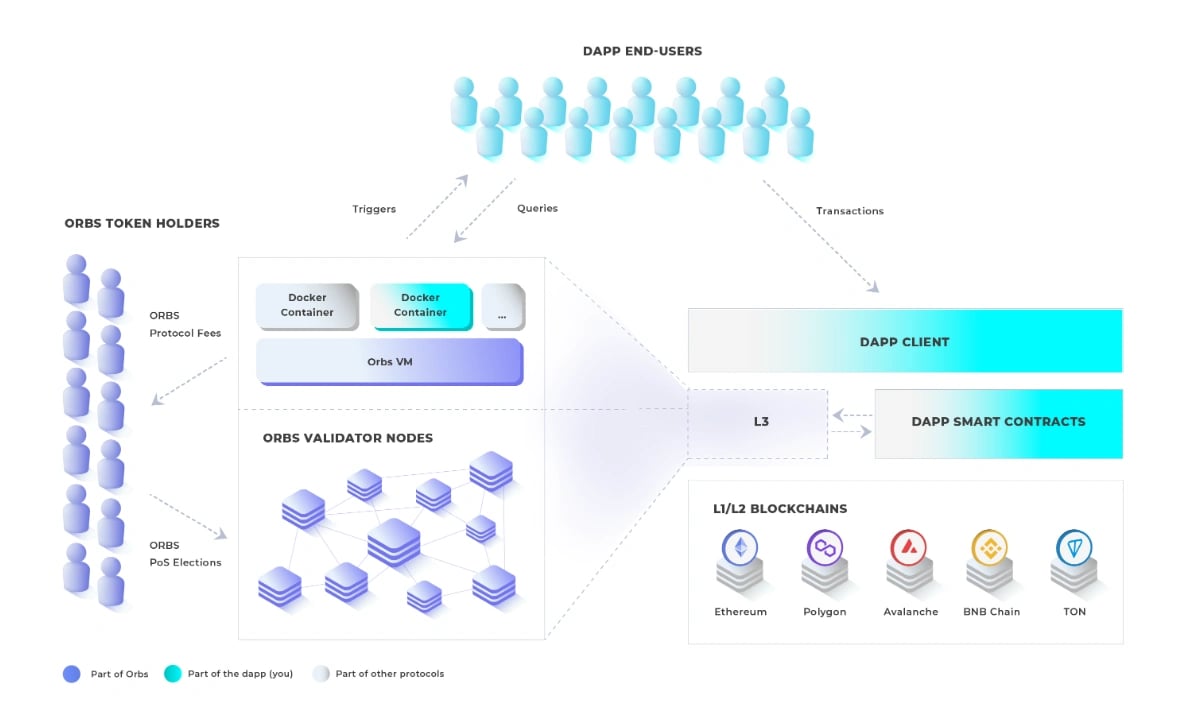
Orbs is an open, decentralized, and public blockchain infrastructure executed by a secure network of permissionless validators using Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus. It is set up as a separate decentralized execution layer operating between existing L1/L2 solutions and the application layer, as part of a tiered blockchain stack, without moving liquidity onto a new chain. [1]
Acting as a “decentralized backend”, Orbs aims to enhance the capabilities of existing EVM and non-EVM smart contracts and open up new possibilities for Web 3.0, DeFi (Decentralized Finance), NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), and GameFi. [2]
Overview
Orbs was launched in 2019, with the aim to tackle the growing concerns regarding the security and governance of DeFi, Web 3 protocols, and dApps (decentralized applications), as projects increasingly rely on centralized backend infrastructure due to the limitations of smart contracts. The Orbs Network functions as a decentralized serverless cloud platform to empower developers to enhance their smart contracts with Layer 3 (L3) decentralized backend services. These services are executed by Orbs' Proof-of-Stake validators, known as Guardians, eliminating the need for centralized backend solutions. As a layer 3 protocol, Orbs runs over existing L1 and L2 blockchains, focusing on providing services to existing DeFi applications for further decentralization and enhancing its capabilities. [2][3]
Decentralized Execution Services
Orbs Lambda
Orbs Lambda is a decentralized, serverless cloud function designed to simplify and enhance the execution of smart contracts on the Orbs Network. Similar in concept to AWS Lambda but fully decentralized, it enables developers to implement cloud functions with just a few lines of JavaScript or TypeScript code. These functions are automatically triggered based on scheduled intervals, on-chain events from various L1 blockchains, or HTTP requests. Orbs Lambda complements existing L1 smart contracts, allowing developers to enrich their business logic without compromising decentralization. [8]
Orbs VM
Orbs VM, short for Orbs Virtual Machine, represents a decentralized and dedicated virtual environment, drawing parallels to Docker-based services but with a decentralized twist. In this context, services are encapsulated within containers and deployed across the Orbs Network, where they are executed by network validators. This orchestration resembles the automation seen in AWS EC2 container services. However, what sets Orbs VM apart is its full transparency and decentralization, guaranteeing execution by leveraging numerous independent network validators. [10]
Key Features
- Flexibility in Programming Languages: One notable feature of Orbs VM is its flexibility regarding programming languages. It embraces industry-standard containers like Docker, enabling developers to employ familiar languages such as Go, C++, Rust, JavaScript, Python, and Java. This eliminates the need for mastering specialized smart contract languages or unusual toolchains, making it accessible for developers with existing knowledge.
- Continuous Availability: Orbs VM operates in an "always-on" mode, distinct from event-driven systems. The services within the VM remain continuously active, with the ability to implement event-driven logic within the container itself. For instance, services can actively monitor multiple L1 blockchains by persistently scanning newly published blocks and scrutinizing their content.
- Complementary to L1 Smart Contracts: Orbs VM is designed to complement rather than replace existing L1 smart contracts. It enriches the capabilities of smart contracts without compromising decentralization. DApps with centralized backends can transition to Orbs VM, eliminating centralized bottlenecks from their offerings.[10]
Use Cases
- Price Feeds: Orbs Lambda can fetch real-time data from external sources like Coinbase, Binance, and CoinMarketCap, providing accurate price feeds for dApps. Lambda functions periodically update and aggregate prices on-chain, enhancing data accuracy.
- Mobile Notifications: DApps such as Aave or Compound can use Lambda to send mobile push notifications to users when specific on-chain conditions are met.
- Cross-Chain Governance: Orbs Lambda can access data across multiple blockchains, enabling dApps to calculate governance votes based on historic balance snapshots. Users on different blockchains can participate in votes, enhancing decentralization.
- Auto Compounding: Lambda functions automate DeFi vault strategies like auto compounding. They monitor triggers and execute on-chain actions, such as reinvesting rewards or reallocating assets based on the best Annual Percentage Rate (APR).
- TWAP Execution: Orbs Lambda optimizes large trades in DeFi by implementing Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP). It divides trades into smaller parts over time, reducing price impact and minimizing losses. The lambda adjusts trade parameters to avoid front-running and maintain market prices.[9]
Protocols/Products Powered by Orbs
Liquidity Hub
Liquidity Hub is a decentralized optimization layer that operates above Automated Market Makers (AMMs). It accesses additional liquidity sources through on-chain solver auctions and decentralized orders via API. These sources include third-party solvers using on-chain liquidity and institutional traders utilizing decentralized limit orders. This allows DEXs to attempt to execute trades more efficiently, reducing the impact of AMM prices. If Liquidity Hub fails to find a better price, trades will proceed through the AMM contract as usual. By doing so, this layer aims to mitigate the problem of fragmented liquidity in DeFi, enabling DEXs to tap into external liquidity sources in order to provide better prices on swaps. [11]
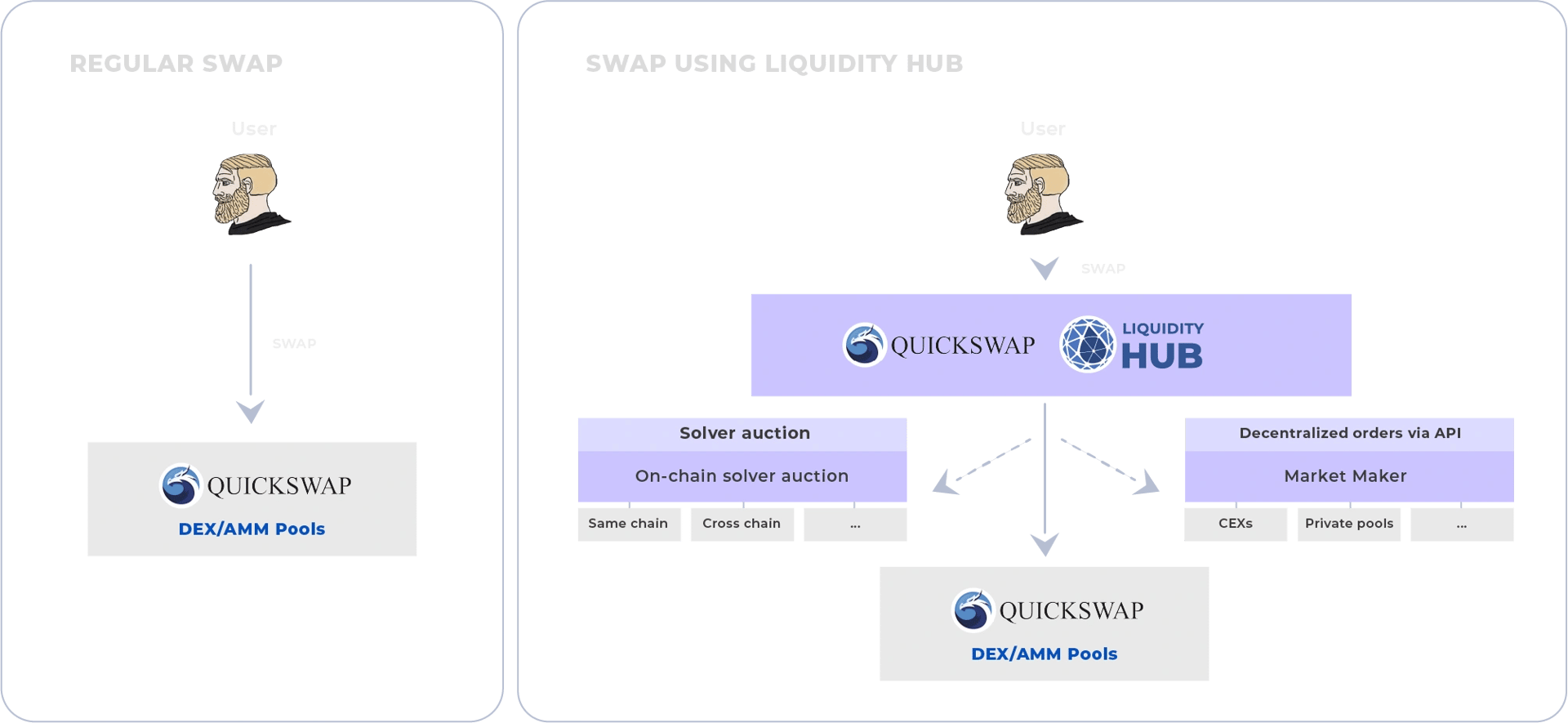
dTWAP Protocol
The dTWAP Protocol introduces a decentralized on-chain solution for executing advanced time-spread algorithmic trades, reducing large order impacts on the market. It leverages the Time-Weighted Average Price (TWAP) strategy, which divides orders into smaller trades executed over time to minimize price impact. This protocol is designed to operate fully decentralized and secure, using smart contracts and permissionless bidders. Key components include a user-friendly UI for parameter input, the dTWAP smart contract to hold and execute orders, Orbs Guardians acting as honest bidders, and optional third-party routers for path optimization. Ultimately, the dTWAP Protocol aims to enhance liquidity and trading efficiency on decentralized exchanges. [12][13]
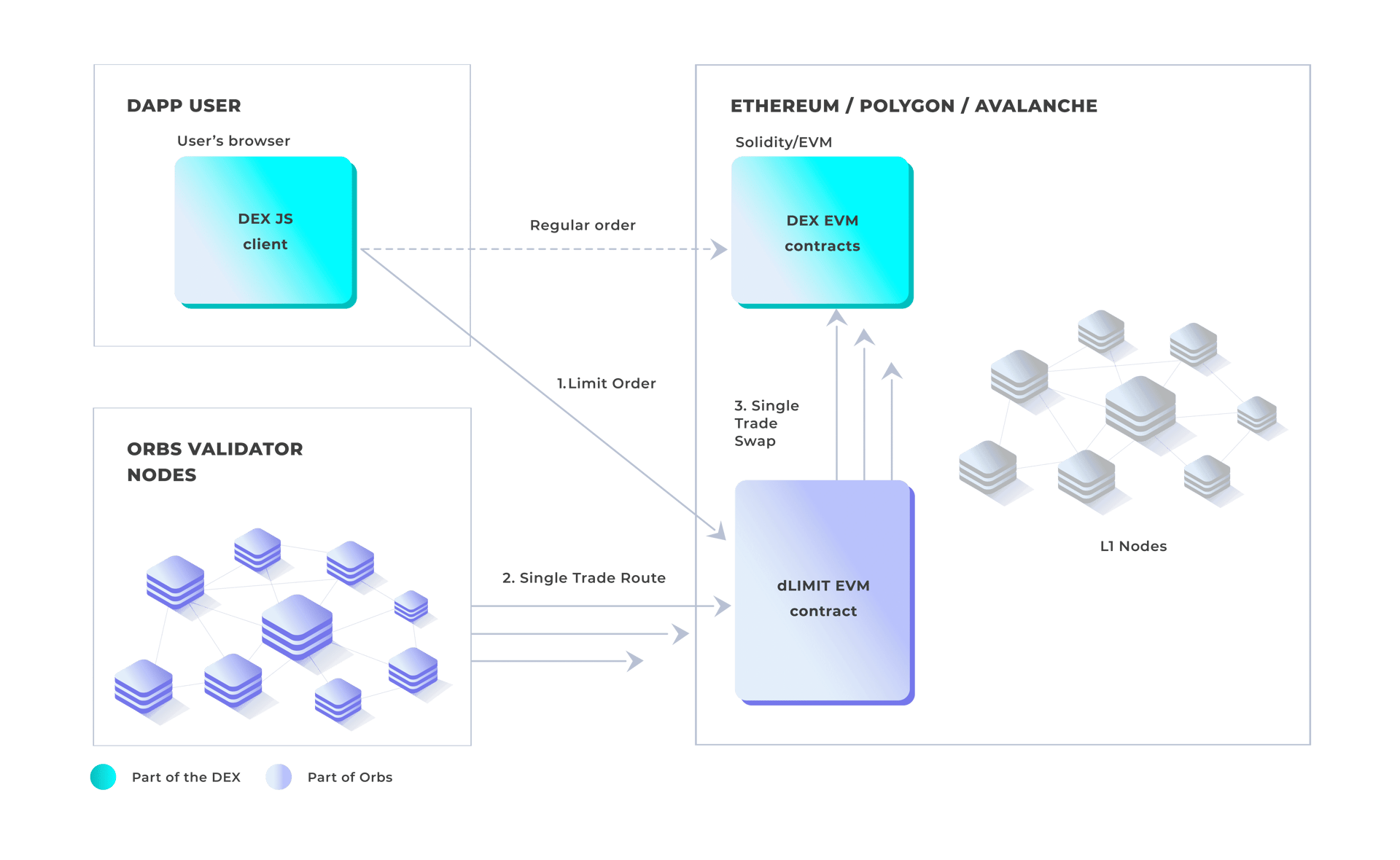
dLIMIT Protocol
The dLIMIT Protocol offers a decentralized on-chain solution for executing limit orders on DEX/AMMs efficiently and reliably. Unlike traditional limit orders, which can be challenging to implement in DeFi, the dLIMIT smart contract ensures optimal execution prices and fair fees. It uses an English Auction bidding mechanism to fill orders at prices close to the user's specified limit. The Orbs network's PoS mechanism guarantees continuous operation with high redundancy and reliability. Anyone can participate as a taker alongside Orbs network validators, providing user protection and decentralized execution for limit orders on DEXs. [14]
The Open DeFi Notification Protocol
The Open DeFi Notification Protocol is a community-led initiative that offers decentralized and cost-free mobile notifications for on-chain events within the DeFi space. Users can easily add notifications for their preferred projects through a straightforward JavaScript web3 class. Notification schemas are continually processed by protocol alert nodes on the Orbs Network. These alert nodes are executed by public validators, providing secure and reliable service. To access these notifications, users have the option to use an open-source iOS and Android app or receive alerts through various communication platforms like Discord, Twitter, and Telegram. [15]
TON.vote
TON.vote is a fully decentralized DAO voting platform designed exclusively for the TON ecosystem, serving as the official DAO voting platform of the TON Foundation. It addresses the governance needs of TON DAOs, projects, and other TON-related communities while upholding the principles of decentralization and transparency. It leverages decentralized storage, relying on TON smart contracts and IPFS, to maintain the integrity of voting data. The system acts as a secondary logical "blockchain" on top of the TON mainnet, with blocks closed daily. Validators from the Orbs Network play a crucial role in adding new blocks, ensuring decentralization and trust. The platform also enables trustless proofs for users, allowing them to verify the authenticity of voting results independently. [16]
Key Features:
- Decentralization: TON.vote allows all users to independently verify the integrity of votes, ensuring transparency and trust in the governance process.
- Gasless Voting: Supporting off-chain voting to enhance user engagement by eliminating the need for users to pay gas fees for voting.
- Advanced Voting Strategies: Users can set conditions for calculating their voting power, such as considering staked tokens only or minimum wallet balances, preventing potential abuse by bots.
- Snapshot: Token holdings are recorded at a specific historic block, preventing manipulation of votes.
- Manipulation Monitoring & Prevention: The platform provides mechanisms to address unforeseen events and abuse during the voting process, such as adding minimum balance requirements to combat bots.
- Verifiable UI: Orbs L3 technology ensures that the displayed votes in the user interface accurately match the data stored in smart contracts, enhancing transparency and reliability.
- Customizable Themed Space Pages: TON.vote offers a space for the community to create customizable project pages with logos and color schemes, fostering community engagement.[17]
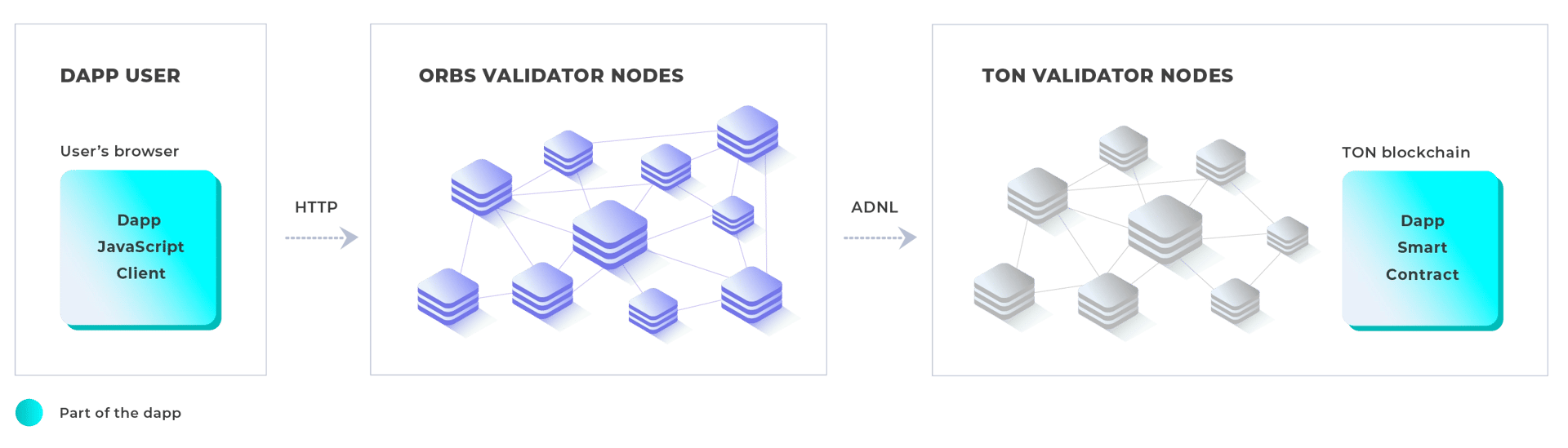
TON Access
TON Access is the decentralized HTTP API for TON, acting as a decentralized RPC network for TON dapps in order to enable HTTP queries to the blockchain state directly from web browsers. It offers unrestricted anonymous access without requiring API keys, ensuring uninterrupted operation for anonymous dapp users. By routing dapp RPC requests through Orbs validators, TON Access maintains decentralized access to the TON blockchain, eliminating reliance on a single centralized entity. [18]
Key Features:
- Unthrottled Access: Unlike RPC gateways like toncenter that throttle anonymous users to 1 request per second, TON Access imposes no such restrictions. This freedom is essential for dapps with anonymous user bases.
- No API Key Required: TON Access provides decentralized access without the need for registering API keys. API keys often involve limitations and cannot be securely stored either client-side or server-side.
- Serverless Operation: Dapp developers need not run their own RPC backend servers, avoiding the centralization that servers bring. This ensures uninterrupted access to user funds, even in the event of devops downtime.
- Decentralized Trust: With dozens of permissionless validators on the Orbs Network staked with over $100 million, TON Access offers trust in a protocol, not a centralized business entity.
- High Redundancy: The API operates through multiple independent Orbs Network validators, ensuring a robust and resilient service with no single point of failure.
- Wide RPC API Support: TON Access supports all RPC API flavors, including HTTP v2, v4, and raw ADNL, catering to the diverse needs of the TON ecosystem.[18]
Network Upgrades
Orbs V1
Introduced in March 2019, Orbs V1 marked the initial implementation of the Orbs PoS protocol. In this version, Orbs executed PoS elections within its own virtual chain, a method commonly employed by PoS networks during that period. Orbs validators conducted these elections, a typical approach in PoS systems. However, this approach had limitations as PoS inherently relies on subjective security, making it less secure than the objective security of PoW. Despite these limitations, Orbs V1 laid the foundation for Orbs' transition into PoS. [25][26]
Orbs V2
Orbs V2, launched in November 2020, represented a significant evolution in the Orbs PoS ecosystem. The key innovation was the integration of Ethereum's PoW security into the Orbs PoS model. Unlike V1, which relied solely on Orbs' validators, V2 introduced an external side-chain, Ethereum, to verify its election results. By leveraging Ethereum's robust security features, Orbs enhanced the integrity and security of its PoS protocol. Ethereum's smart contracts were employed to manage staking, delegations, and reward distribution, ensuring a secure and efficient environment for users. [25][27][28]

Orbs V3
Orbs V3, launched on March 29, 2022, marked the 3rd year anniversary of Orbs' mainnet launch and their first step in multi-chain PoS. Orbs expanded PoS elections to Polygon, making it the world's first PoS implementation spanning three chains: Orbs, Ethereum, and Polygon. The primary motivation behind Orbs V3 was to address the rising gas costs associated with Ethereum, thereby increasing accessibility for users, particularly those with smaller stakes. By leveraging Polygon's scalability and compatibility with Ethereum smart contracts, Orbs aims to enhance the network's usability and efficiency. Orbs V3 ensures a secure and cost-effective environment for staking and delegations across multiple chains, making it a notable milestone for Orbs. [29][30]
ORBS Token
The ORBS token serves as the primary means of payment for utilizing the services provided by the Orbs platform. Users can use ORBS to compensate infrastructure operators (Validators) for executing tasks related to the consensus layer, smart contracts, and consensus-based storage. Additionally, the token plays a crucial role in Orbs' proof-of-stake ecosystem by enabling users to participate in the election of Validators responsible for network security and governance decisions. [24]
The ORBS token functions as an ERC-20 token within the Ethereum network, featuring a total fixed supply of 10 billion tokens. Orbs has adopted a sustainable strategy, avoiding inflationary token supply practices, and instead, upholding the network's long-term viability through operational fees. The token distribution event (TDE) occurred on March 28th, 2019, coinciding with the initial launch of the Orbs network. This distribution process allocated tokens to their respective pools, facilitating the development and growth of the Orbs ecosystem. [24]
Token Distribution
Long-term Reserves (55%)
These tokens, totaling 5.5 billion, were vested over 55 months following the Token Distribution Event (TDE). They are designated for network development, ecosystem expansion, and Proof-of-Stake rewards.
Private Sale (20%)
This pool consists of 2.0 billion tokens with no lock-up or vesting period. It was part of the pre-TDE private sale aimed at project funding, including research and development, core technology development, ecosystem creation, operations, business development, and marketing.
Team and Founding Partners (20%)
2.0 billion tokens, representing 20% of the total supply, were vested over 36 months following the TDE, with an initial lock-up period of 6 months. These tokens are allocated to Orbs' team members and founding partners.
Advisors (5%)
This pool includes 0.5 billion tokens that were vested over 12 months following the TDE, reserved for external project advisors.[24]
Partnerships
On July 6, 2023, Orbs expanded its ecosystem by integrating with Pendle Finance through the Open DeFi Notification Protocol. Pendle Finance offers a platform for tokenizing and selling future yields. Pendle users can now set up "New Market" notifications, staying updated in real-time when new markets are deployed on Pendle Finance. This partnership enhances accessibility to DeFi opportunities and information for Pendle users. [19]
On July 17, 2023, Orbs partnered with Chronos, integrating their dLIMIT and dTWAP trading orders with the Chronos DEX. Chronos DEX, one of the largest DEXs on Arbitrum, allows traders to employ advanced order types, guaranteeing order prices or breaking up large orders into smaller trades. Chronos users are able to access both dLIMIT and dTWAP order types, allowing them to secure the order price or divide substantial orders into smaller transactions. [20]
On July 20, 2023, Orbs partnered with Convex Finance to further expand their DeFi capabilities through the Open DeFi Notification Protocol. Convex Finance, enables Curve.fi liquidity providers to earn trading fees and boost CRV without locking their CRV tokens. Through the integration, Convex users can set up "Staking Unlocked" notifications, ensuring they never miss the end of their CVX token locking periods. [21]
On August 21, 2023, Orbs entered into a strategic partnership through the integration of Curve Finance on the Open DeFi Notification Protocol. Curve Finance is a prominent DeFi protocol offering high liquidity, low slippage, and low-fee transactions for ERC-20 tokens. This collaboration allows Curve users to set up "Staking Unlocked" notifications, keeping them informed about CRV token unlocking periods. [22]
On September 15, 2023, the ORBS token was made available on the Chronos DEX through the use of the Satellite cross-chain bridge by Axelar. This integration enables token swaps between Ethereum, BSC, and more. Users can now swap and add liquidity to Orbs pools on Chronos, further enhancing the token's reach and liquidity in the DeFi space. [23]
Team
The project's core team consists of more than thirty dedicated contributors spanning from Tel Aviv, London, New York, Tokyo, and Seoul.
Founders
- Daniel Peled: President & Co-founder
- Tal Kol: Co-founder
- Netta Korin: Co-founder
- Uriel Peled: Co-founder
Senior Team Members
- Rotem Yakir: DeFi & NFTs Developer
- Yuval Aviguy: Software Engineer
- Doron Aviguy: Software Engineer
- Ami Hazbany: Blockchain Developer
